In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Cell Structure of Saccharomyces 2. Vegetative Body of Saccharomyces 3. Reproduction 4. Life Cycle Patterns.
Cell Structure of Saccharomyces:
The genus Saccharomyces (Gr. Saccharon, sugar; mykes, fungus) consists of about 41 species. 5. cerevisiae, commonly known as Brewer yeast or Backer’s yeast is used widely in wine and baking industry.
It produces two types of enzymes: an extracellular invertase and an intracellular zymase. The invertase hydrolyses canesugar to dextrose or invert sugar and zymase breaks invert sugar into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
Vegetative Body of Saccharomyces:
The thalloid plant body is unicellular, but during rapid multiplication by budding the cells may remain attached in chain forming pseudo- mycelium (Fig. 4.38). The cells may be globose, elliptical, oval to even rectangular in shape and measure about 5-6 x 6-8 µm.
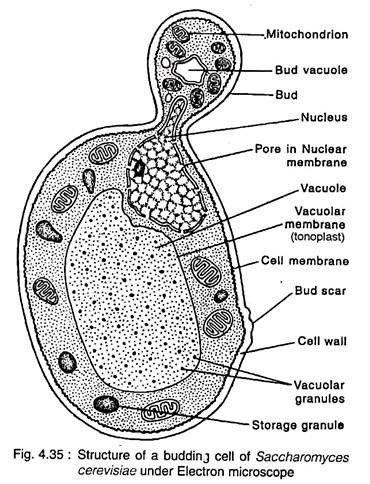
Electron microscopic studies (Fig. 4.34, 4.35) and chemical analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae show that the cells are surrounded by a distinct cell wall with three layers. The outermost layer mainly consists of protein-mannan and some chitin; the middle layer mainly of glucan and the innermost layer consists of proteinglucan.
Some phosphate and lipids are also present, while cellulose is absent in the cell wall. Inner to the cell watl is the cell membrane (plasmalemma), i.e., an usual unit membrane having series of shallow, elongated pits or invaginations (Fig. 4.35).
In the centre, the cell having a large central vacuole, limited by a single membrane, the tonoplast, which contains a watery substance, granules of polymetaphosphate and lipid.
The cytoplasm is granular and contains organelles like nucleus, mitochondria, golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome and other substances like glycogen bodies, volutin granules, oil globules etc.
Some hydro- lytic enzymes like proteases, esterases, ribonuclease etc., are also present in the cytoplasm. The nucleus having outer perforated double unit membrane remains by the side of the vacuole. The nucleus is bipartite in nature having major Feulgen positive and a smaller Feulgen negative regions (Moor and Muhlethaler, 1963).
Reproduction in Saccharomyces:
Saccharomyces reproduces by vegetative, asexual and sexual means.
A. Vegetative Reproduction:
Vegetative reproduction takes place by fission and budding.
(a) Fission:
It takes place during favourable condition. In this process, single vegetative cell forms two daughter cells of equal size (Fig. 4.36). During fission, a constriction appears in the middle of the cell and simultaneously nucleus undergoes mitotic division.
Both the steps progress simultaneously. After nuclear migration, one at each side, partition wall forms almost in the half way of the mother cell and, as such, two daughter cells are formed.
(b) Budding:
Budding also takes place during favourable condition. The protoplasm of vegetative cell swells up at one side in the form of a bud (Fig. 4.37). The nucleus undergoes mitotic division. Out of two nuclei formed by mitosis, one goes to the bud and other one remains in the mother. Bud enlarges and eventually cuts off from the mother by partition wall.
The size of the bud is always smaller than the mother cell. After maturation, these bud separate from the mother and leave a convex scar on the surface, called bud scar. Similar scar with concave surface remains on the wall of the bud, called birth scar.
Sometimes due to rapid division, large number of buds develop without being detached from one another and persist in the form of branched or unbranched chain, called pseudo-
mycelium (Fig. 4.38). Finally the cells get detached and grow individually.
B. Asexual Reproduction:
It takes place during unfavourable condition by the formation of thick walled spore, called endospore (Fig. 4.39). During this process nucleus divides mitotically and forms four nuclei. The protoplast divides into four units, each with one nucleus and forms four endospores. During favourable condition, endospore germinates by budding and buds grow individually.
C. Sexual Reproduction:
Sexual reproduction takes place during unfavourable condition. In this process, two vegetative cells or ascospores behave as gametangia (Fig. 4.40). Two such cells come very close and develop beak-like outgrowth towards each other. Both the outgrowths come in contact and the intervening walls between them dissolve.
The nuclei of both the gametangia come to the fused outgrowth (conjugation tube) and they fuse therein to form a diploid zygote. The zygote behaves as an ascus. The diploid nucleus of zygote undergoes meiotic division forming 4 or 8 (with additional mitosis) ascospores. The ascospores are liberated by breaking the ascus wall and behave as somatic cell.
Life Cycle Patterns of Saccharomyces:
Three patterns of life cycle are found in yeast:
Haplobiontic, diplobiontic and haplodiplobiontic (Fig. 4.41):
1. Haplobiontic Type:
This type of life cycle is characterised by more elaborate haploid phase than the diploid phase, found in Schizosaccharomyces octosporus (Fig. 4.41 A). The diploid phase is restricted only in the zygote. The vegetative cells are haploid and behave as gametangia.
Two such gametangia fuse together and form a diploid cell. The diploid cell behaves as an ascus whose nucleus divides first meiotically, then mitotically; results in the formation of eight ascospores. After maturation, the ascospores liberate by bursting the ascus wall. The ascospores then behave as vegetative cell and continue multiplication through budding.
2. Diplobiontic Type:
This type of life cycle is characterised by more elaborate diploid phase than the haploid phase, found in Saccharomycodes ludwigii (Fig. 4.41 B). The haploid phase is restricted only in ascospore, with short duration. The ascospores behave as gametangia and, without liberating from ascus, they unite in pair. The paired gametangia after fusion produce diploid zygote.
The zygote then germinates by producing germ tube which comes out through the ascus wall. The germ tube becomes multicellular from which diploid sprouts develop by budding. After detachment from the mother, the diploid sprouts function as asci and produce four ascospores by reduction division.
3. Haplo-Diplobiontic Type:
This type of life cycle is represented by haploid and diploid phases, of more or less equal duration, found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Fig. 4.41 C). The haploid cells of opposite mating type normally multiply by budding. Two such cells of opposite mating behave as gametangia and undergo fusion. The fused gametangia develop a diploid zygote.
The diploid zygote like the haploid cells undergoes budding and forms many diploid cells. With the scarcity of food, the diploid cell behaves as an ascus and by reduction division it forms four haploid ascospores. After liberating from the mother wall, the ascospores undergo budding and form many haploid somatic cells.