The following points highlight the top six plant promoters for genes. The promoters are: 1. Core Promoter 2. Light Responsive Promoters 3. Stress Responsive Promoters 4. Plant Hormonal Responsive Promoters 5. Sucrose Responsive Promoters 6. Low-Oxygen Responsive Promoters.
Contents
1. Core Promoter:
Core promoter elements are defined as minimal promoter that contain TATA box. These are indispensable for initiation of transcription by RNA Pol II. One of the most well defined core promoter elements in plant is TATA box, situated at about -20 to -35 from transcription initiation sites (TIS) like those of animals. This cis-acting box regulates binding of transcription factor (TFIID) complex to TIS.
Consensus TATA sequence between many plant promoters and other eukaryotic systems have shown high degree of similarity. Several DNA binding proteins specifically bind to the regions are commonly referred as TATA box binding proteins (TBPs) have amino acid sequence related to TBPs of animals. Apart from TBP, several general transcription factors have been cloned and characterized from plants.
Another promoter elements involved in basic transcription initiation are downstream promoter elements (A/G) G (A/T) CGTG, located at position +30 bp downstream of the TATA less TIS. Similarly, prl promoter containing conserved GC-rich element upstream of TATA box was described in barley plant. Two more regulatory elements known as GC box and CAA T box when present contribute significantly in the initiation of transcription frequently, which are located around -100 bp to TIS.
The GC box, GGGCGG, has been located in the upstream promoter of many plant groups. The well conserved CCAAT box is present -80 to 150 bp upstream of TIS. In plant promoters, signal for the direction of gene expression is located in a compact region, less than 1000 bp upstream of the TIS. The promoters of house-keeping genes like ubiquitin are active known to be expressed constitutively.
2. Light Responsive Promoters (LRPs):
Light responsive gene in expression is mainly focused on two processes. One of its roles is in photosynthesis and second is in light regulated photomorphogenesis. Plants are loaded with varieties of photoreceptors like phytochromes, blue light receptors, and receptors for UV light often responsive to quality of light signals involved in signal transduction pathways, which consequently regulate transcription of several genes that encodes proteins involved in photosynthesis and developmental process.
It is generally presumed that various light activated pathways target different light responsive elements including targeting of common LRFs, deletion analysis of promoter region of light induced genes containing several cis-acting elements participate in the control of light regulated gene expression.
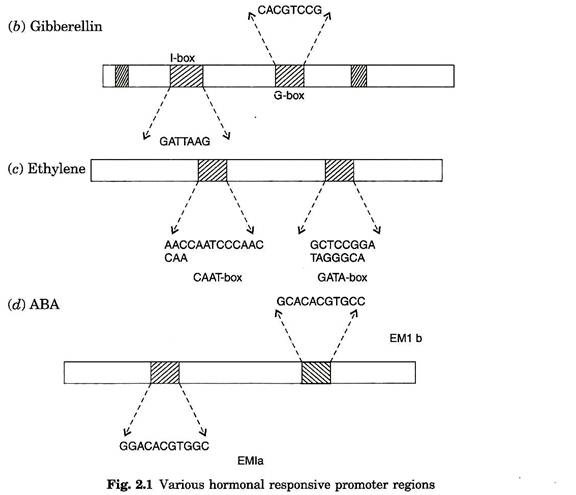
Atleast four important components of light responsive promoters have been identified. They are GT-I box (GGTTAAA), originally I-box (GATAAAG), G-box CACGTGCCTACC identified in pea ribulose bis phosphate carboxylase rbcS-3A gene promoter. This is known to be involved in turning off the expression of gene in the dark.
GT-I has also been identified in several other genes which encode proteins participating in photosynthesis and certain secondary metabolite synthesis. The I box motif is required for phytochrome regulation. Certain bZiP transcription factor proteins known as G- box binding factors specifically bind to G-boxes.
In addition, several other transcription factors commonly known as Arabidopsis factors like H45 and PIF3, important in light mediated regulation strongly exhibit preferential binding with G-box. The factor PIF3 is known to bind with phytochrome B after conversion into active form. Several light responsive plant promoters also contain AT-rich motifs.
These regions are specifically meant for binding with High Mobility Group (HMG) proteins represented with AT-hook domains. Presence of AT rich motif can influence the promoter activity in either positive or negative way. In pea plants, the promoter of rbc-3A and GS2 (Glutamine synthetase) gene contains AT sequences, functions as activation elements. Presence of H-box in certain cis-acting element is essential for light and elicitor regulation.
However, presence of H-box is unimportant in light regulated genes that are not involved in flavonoid biosynthesis. Certain chloroplast located light responsive dehydrogenase gene contains three copies of Gap box. The consensus sequences of Gap box are found to be 5′ CAAATTGAA (A/G) A-3′. This cis element is also found in other phytochrome gene promoter.
3. Stress Responsive Promoters (Biotic and Abiotic):
Biotic Stress Responsive Promoter:
Increasing evidence indicates that many plants exhibit measured response against wound pathogen attack. Large numbers of pathogen inducible genes and their promoter have been studied in plants. Several plant derived agents such as salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), methyl jasmonate (MeJA), and other microbial elicitors act as signalling molecules. Exogenous applications of these agents or pathogen elicitor can trigger expression of pathogen-related (PR) proteins.
Several of these defense related gene promoter contain unique biotic responsive elements. In soybean, MeJA responsive region (JARE) has been identified in the promoter of the VSPB gene, which is responsive to MeJA and sugar and the region was located between -535 and -585 bp. The promoter region of barley lipoxygenase 1 and potato pin 2 proteinase inhibitor II genes contains bZiP protein-binding boxes (TGACG) in the same localized region.
Another major class of cis-acting elements present in the pathogen defense genes is W-boxes. This region has been identified during system acquired resistance. Expression of pathogen inducible genes requires participation of W-box binding WRKY factor proteins. In wound responsive gene expression, both WRKY transcription factor and GCC like elements has been implicated suggesting common signalling mechanism for wound and pathogen induced gene expression.
Abiotic Stress Responsive Promoter:
Heat stress responsive promoter:
Response of plants towards heat stress is well conserved. Plants contain several types of heat shock genes and their promoters also contain heat shock genes and their promoter regions contain heat shock response elements (HSE). These elements contain unique palindrome motif of nGnnTTC and nnGAA and play a crucial role in heat shock response in several plants.
These are very close to TATA box about between 15 and 18 bp. However, certain petunia HSP genes lack TATA box. Some plant HS genes contain CAAT box located about 50-100 bp upstream region. In addition, AT-rich sequences are also found in many plant HS genes. A number of HS transcription factors (HSF) that specifically bind to HSE have been determined and their domain for DNA binding is well conserved among plants.
Cold Responsive Promoters:
Cold responsive genes on plants contain conserved motif CCGAC promoter region. Cold responsive genes are also responsive to abscisic acid and drought, which strengthen the evidence of cross talking of genes against abiotic stress. In Arabidopsis, cold responsive corl5a genes promoter is responsible for ABA, drought and cold responsiveness, but these sequences are inactive in normal condition.
Most of the cold responsive gene promoters contain dehydrogenase responsive elements (DRE) with a CCGAC conserved motif present in number of copies. Mutation in these regions results in the complete loss of promoter activity in winter Brassica maps cold responsive gene BN115.
Drought (Dehydration) Responsive Promoters:
Plants are exposed to water deficient condition due to prevalent drought. Many drought responsive genes contain dehydration responsive elements (DRE) with a CCGAC conserved motif. Cold responsive genes also contain DRE elements with the same C-repeat. Expressions of drought and cold stress inducible genes are trigged by ABA signalling or ABA independent signaled transduction pathway. This stress relieving gene contains a potential ABRE (ACGTGG) in their promoter region.
The G-box in Arabidopsis requires both dehydration and cold responsiveness. In addition to drought responsive genes, several other genes like LEA are induced by ABA hormones. Water deficient or desiccation condition can activate these genes. In Arabidopsis thaliana stress relieving genes such as rd 29A and rd 29B genes have cis-acting element (5′ TACCGCACAT 3′) as well as ABRE. These promoter core regions play different roles in regulating rd genes during progressive drought stress.
4. Plant Hormonal Responsive Promoters:
Auxin Responsive Promoter:
Auxin plays a significant role in performing various physiological functions including growth, apical dominance and differentiation etc. It executes functions by acting as signal molecule. Auxin induced gene expression has shown that new mRNAs are synthesized after ten minutes when plant tissues are treated with auxin.
Several auxin responsive genes contain promoter with a unique cis element, have been characterized in pea PS-IAA5/5 gene, the soybean GH3 gene and SAUR15A (Soybean Auxin UPRNA). Many cis-acting motifs have been identified in auxin responsive genes such as GTCCCAT with pea PS- IAA4/5 promoter and TGTCTC with the soybean GH3. Similarly, TGTCTC and TGTCCAT elements are present within soybean SAUR15A promoter.
This first AuxRE was the octopine synthase (ocs) element consisting of 20 bp sequences 5′ TGACGTAAGCGCTGACGTA 3′. Presence of two imperfect TGACGTCA palindromes has received much attention. Certain auxin inducible promoters, GH3 and PS-IAA 4/5 contain more than one AuxRE, acting independently. In addition, some auxin inducible promoter contains G-boxes and/or TGA boxes and promoters binding specifically to this are present in plant nuclear extract (Fig. 2.1).
Gibberellin Responsive Promoter:
One of the most widely studied gene expression mechanism in plant is the gibberellins signal mediated expression of alfa amylase gene promoter, conceived well by gibberellins, contains GARE motif (Gibberellic Acid Responsive Elements) TAACA, TATCCAC box and pyrimidine box CTTTT.
Extended analysis of promoter shows that its gene promoter motif i.e., TAACA resembles c-myb consensus binding site. Presence of pyrimidine box TAACA and TATCCA box has been identified in wide varieties of cereal alfa amylase promoter. The alpha amylase promoter region contains sequences that bind several nuclear proteins that are targeted to TAACAGA and TATCCAT boxes in a barley alpha amylase promoter.
The alpha amylase gene promoter of wheat contains pyrimidine box and TAACAGA box to which nuclear proteins binds. Similarly, wheat and barley alpha amylase gene promoter encloses both ABA and GA responsive sequences situated very close to each other, indicated that ABA antagonizes GA induced expression of alpha amylase gene.
Ethylene Responsive Promoters:
Ethylene is a gaseous hormone involved in the ripening of fruits and abscission, besides its defensive role against pathogen attack. Expression of ripening related genes contains ethylene responsive promoters. During pathogen attack, ethylene production increases and several defense related genes are expressed which encodes pathogenesis related (PR) proteins.
Promoter region of PR genes contain conserved sequences of 5′ TAAGAGCCGCC 3′ and these are generally referred as GCC box. Some PR genes contain two GCC box in their promoters. Loss of GCC box in PR genes resulted in the lack of ethylene responsive in PR promoter. It has been demonstrated that gene construct composed of two tandem copies PR promoter contains GCC boxes confirmed ethylene response.
The core GCC box is closely associated or a part of Ethylene Responsive Element (ERE). Many nuclear proteins are able to bind to the GCC containing ERE region of PR genes. At least four proteins specifically interact with GCC box and are referred as Ethylene Responsive Element Binding Proteins (EREBP). The domain present in these EREBP are similar to transcription factors, regulate gene expression in seed and floral organ development.
Interestingly, ripening and senescence responsive genes that contain ethylene responsive promoter do not contain GCC boxes, indicating the presence of more than one ethylene responsive elements. Presence of additional G-boxes in certain PR gene promoter influence ethylene responsiveness.
Abscisic Acid Responsive Promoter:
ABA induced gene contains multiple Abscisic Acid Responsive Elements (ABREs), predominantly having G-box with 5′ ACGTGGCG 3′ sequences. Some of the ABA inducible genes like wheat EM, barley HVA 22, rice Osem genes contain multiple ABRE sequences, of which notable motifs are CACGTGGC (EMIa) and CACGTGCC (EMIb). In this system, transcription factor AbZiP is specifically bound to the EMIa element but not EMIb. Both G-box and E-boxes (CACGTG) are present to this bZiP and bHLH proteins (Fig. 2.1).
5. Sucrose Responsive Promoters (SURs):
Sugar plays a central role in controlling plant metabolism, growth, development and signalling. Battery of plant genes contains sucrose responsive promoters which codes for cereal alfa amylases, sweet potato storage proteins, sucrose synthesis etc. Sucrose responsive element AATAGAAAA and AATACTAAT. Similarly, TACTATT (sps) motif was present in the promoter of potato β amylase gene (Table 2.1).
Table 2.1 Promoters involved in special regulation of gene expression
6. Low-Oxygen Responsive Promoters:
Higher plants are able to show response to low oxygen condition by inducing expression of specific set of genes. Some of the prominent responses shown by the plant are the expression of alcohol dehydrogenase gene (Adh). Expression of this gene is influenced by abiotic stress factors.
The most prominent and specialized low oxygen response or anaerobic-responsive region in the Adh promoter in anaerobic condition is GT motif (GGTTT) and GC motif GCC transcription factor like AtMYB2 was shown two separate motif in Arabidopsis Adh gene.