In this article we will discus about the asexual and sexual modes of reproduction in paramecium with the help of suitable diagrams.
Paramecium in Binnary Fission (Asexual Reproduction):
1. It is a slide of Paramecium showing asexual mode of reproduction.
2. It occurs during favourable conditions when food is available in large quantities and temperature is favourable.
3. A median constriction starts developing in the cytopharynx region.
4. The cytopharynx is divided into two each half develops the missing part.
5. The macronucieus elongates and the divides through constriction amitotically.
6. The micronucleus divides mitotically.
7. Ultimately one Paramecium gives rise to two daughter paramaecia.
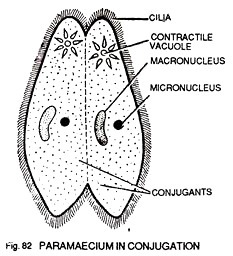
Paramecium in Conjugation (Sexual Reproduction):
(1) In conjugation (sexual reproduction) the two paramaecia come in contact and unite through the edges of their oral groove.
(2) The pellicle, all along the union of two forms, is disintegrated. At this stage they are called gametocytes or conjugant.
(3) The macronucieus of each conjugant disappears and their micronucleus divides twice and forms 4 haploid micronuclei.
(4) Out of these four micronuclei three daughter micro nuclei disintegrate, while remaining one divides into two unequal daughter pronuclei. Of these, the smaller one is the active male migratory pro-nucleus, whereas the larger one is the stationary female pro-nucleus.
(5) The migratory male pro-nucleus of each conjugant moves through the protoplasmic bridge into the other conjugant and ultimately fuses with stationary female pro-nucleus forming zygote.
(6) The nucleus of zygote is diploid and is called amphinucleus and this type of mixing of two nuclei from different individuals is called amphimixis.
(7) After zygote formation the nucleus continue division and forms four daughter paramecia.
(8) The conjugation occurs only when nutrition is deficient and when temperature of water is below the optimum.
(9) Conjugation results in rejuvenation and transference of hereditary materials and occurs in different strains.