In this article we will discuss about the structure of RNA.
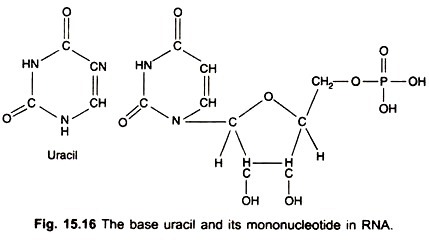
RNA is a long un-branched polynucleotide chain chemically similar to DNA except for two major differences. The sugar in DNA is a deoxyribose, in RNA a ribose. Out of the 4 nucleotides, three (G, C and A) are identical in DNA and RNA. The fourth is thymine in DNA, whereas in RNA the closely related pyrimidine uracil is present (Fig. 15.16).
RNA molecules are usually single stranded and do not have complementary base ratios. The amount of adenine is often not equal to the amount of uracil, and the amounts of guanine and cytosine are also not always equal. Modified bases such pseudouridine (ψ) and methylated bases are present; these are particularly abundant in tRNAs.
The products of transcription are 3 types of RNA, namely transfer RNA (tRNA), heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) all of which are involved in protein synthesis.