The upcoming discussion will update you about the difference between nitrate and sulfate respiration.
Difference # Nitrate Respiration:
Nitrate respiration is typically carried out by some facultatively anaerobic bacteria, like Paracoccus denitrificans, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Ps. stutzeri, Ps. aeruginosa, Bacillus cereus, B. licheniformis, Thiobacillus denitrificans etc. All of them can also grow aerobically carrying out normal aerobic respiration, but they possess an additional faculty of using nitrate, only in absence of air, as an alternative terminal hydrogen and electron acceptor, resulting in an anaerobic nitrate respiration. In this process, nitrate is reduced to molecular nitrogen or nitrous oxide or even nitric oxide.
Hence, nitrate respiration is also known as de-nitrification. Because, through the process, nitrate, which is a valuable nitrogen source for plants, is lost mostly in the form of molecular nitrogen from soil. De-nitrification is considered a wasteful phenomenon.
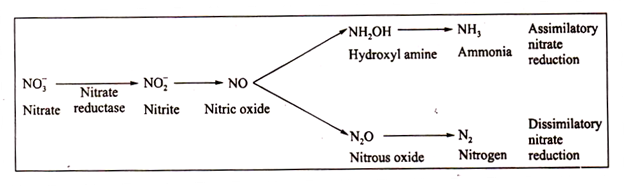
Plants, fungi and many bacteria are able to use nitrate as a nitrogen source for protein synthesis. They carry out the process of assimilatory nitrate reduction whereby nitrate is reduced in a step-wise manner to ammonia. In contrast, in nitrate respiration, the organisms carry out dissimilatory nitrate reduction, the product being molecular nitrogen, nitrous or nitric oxide.
The two pathways have some common intermediates and then they diverge as shown:
The intermediates and the enzymes of nitrate reduction are not well-established. However, the first enzyme, nitrate reductase, catalyzing reduction of nitrate, to nitrite is well-known. An interesting feature is that this enzyme has been found in soluble form in assimilatory nitrate reduction and particle- bound in dissimilatory nitrate reduction in the same organism.
The particle-bound enzyme is synthesized only when the organism is growing in absence of free oxygen. Thus, though the early intermediates are common in both the pathways, there may be basic differences in the pathways which are not well-known.
Difference # Sulfate Respiration:
The ability to carry out sulfate respiration is restricted to some bacterial organisms and all of them are obligately anaerobic. They mainly belong to the genera Desulfovibrio and Desulfotomaculum. Like nitrate reduction, reduction of sulfate also takes place by the assimilatory and dissimilatory pathways. Plants, fungi and bacteria, in general, are able to use sulfate as source of the essential element, sulfur, which is used in the synthesis of sulfur-containing amino acids, like cysteine, and methionine.
In the assimilatory sulfate reduction pathway, sulfate is reduced in a stepwise manner to sulfide (S2-) which is incorporated into amino acids. In the dissimilatory sulfate reduction also the end- product is sulfide. An enzyme ATP-suIfurylase catalyses transfer of sulfate to AMP forming adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (APS) and pyrophosphate.