The below mentioned article includes a list of four simple experiments on osmosis.
1. Experiment to demonstrate the osmosis by using sheet of cellophane or goat bladder:
Requirements:
Beaker, thistle funnel, goat bladder or sheet of cellophane, thread, water and sugar solution.
Method:
1. Cover the lower opening of the glass tube with the goat bladder or sheet of cellophane and tie it with the thread.
2. Fill in the interior of the tube with molasses, a concentrated sugar solution in water.
3. Place the whole apparatus in a beaker containing water, preferably distilled water.
4. Note the level of the water in the thistle funnel and keep the apparatus to note the results.
Observations:
Level of the water in the thistle funnel increases (Fig.2).
Results:
1. Movement of water through the goat bladder or cellophane sheet into the thistle funnel takes place.
2. Water concentration in beaker is 100% while in the sugar solution it is less than this, and, therefore, the water from the region of higher concentration moves towards the region of lower concentration. The movement is through a semipermeable membrane and so the experiment shows the phenomenon of osmosis.
3. The force, with which the solution level in the tube increases, arises from the pressure exerted by the diffusion of water molecules into the tube. This pressure is called osmotic pressure.
4. Stability of the water level in the funnel indicates that water concentration in both the beakers as well as funnel is same and thus osmosis stops.
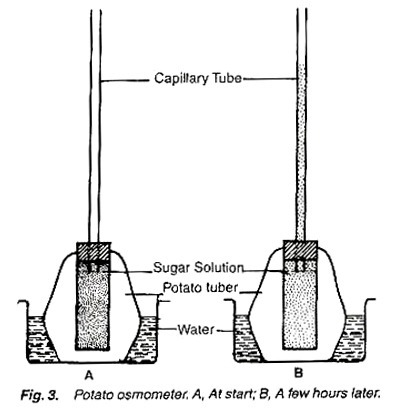
2. Experiment to demonstrate osmosis with the help of potato osmometer:
Requirements:
Petri-dish, water, potato, sugar solution, cork and capillary tube.
Method:
1. Take a potato tuber, remove its outer covering from one end and cut the same end flat.
2. Scoop out a cavity from the other end of the tuber running almost upto the bottom.
3. Fill the cavity with the sugar solution and fit an airtight cork fitted with a capillary tube on the upper end of the cavity (fig. 3).
4. Place the capillary- fitted potato tuber in the water- filled petri-dish.
5. Mark the solution level in the tube and watch the experiment for some time.
Observations:
After some time the level of the solution in the tube increases. Mark the level of solution when it stops to move.
Results:
The level in the capillary tube increases because of the fact that osmotic pressure of the sugar solution is higher than that of the water, and the water moves through the semipermeable membrane of potato from petri-dish into the cavity. So the experiment shows that phenomenon of osmosis.
3. Experiment to demonstrate the osmosis by the egg osmometer:
Requirements:
Egg membrane, dilute HCI, water through, graduated tube, sugar solution and stand.
Method:
1. Prepare an egg membrane by carefully removing waterproof shell of egg with the help of dissolving it away in dilute HCI.
2. Remove all the fat and protein-containing yellow material of the egg by making a hole on its one end.
3. Fill the sugar solution in the egg membrane through the hole and fit a graduated tube in the hole.
4. Place the complete apparatus in a water-filled trough (Fig. 4).
5. Note the level of sugar solution in the graduated tube and keep the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
Observations:
Level of the sugar solution increases in the tube.
Results:
The level in the tube increases because of the fact that osmotic pressure of the sugar solution in the egg membrane is higher than that of water, and so the water from the trough passes through the egg membrane into the sugar solution thus increasing its level. Egg membrane is a semipermeable membrane.
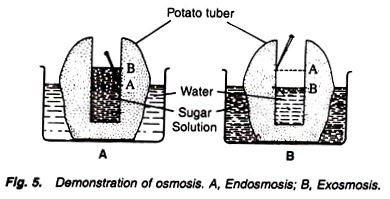
4. Experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of exosmosis and endosmosis:
Requirements:
Potato tubers (2), knife, conc. sugar solution, water, pin, beakers (2).
Method:
1. Remove the outer skin of the tubers and cut their one end flat with a sharp knife.
2. Scoop out a cavity from the other end of the tuber running almost upto the bottom as in experiment No. 14.
3. Fill the concentrated solution of sugar in the cavity of one tuber, and water in the other.
4. Mark the level of the sugar solution and water in the cavities with the help of pins.
5. Place the potato containing sugar solution in a beaker containing water, and the another potato containing water in its cavity in the beaker containing sugar solution (Fig. 5).
6. Keep and observe experiment for some time.
Observations:
The level in the cavity containing sugar solution increases while the level decreases in the another tuber, i.e., in the cavity filled with water.
Results:
The level of the sugar solution in the first tuber increases because of the fact that water moves from the beaker into the cavity through the semipermeable membrane of potato. Thus it shows the phenomenon of endosmosis.
The level of the water in the second tuber decreases because of the fact that water moves from the cavity into the beaker through the semipermeable membrane of potato tuber. Thus it shows the phenomenon of exosmosis.