In this article we will discuss about the process of osmosis in plants.
It is usually seen, that when two liquids of different densities are separated from each other by placing a membrane between them, by which the water of the liquid of lower density flows towards the liquid of higher density, then such separating membrane is called the semipermeable membrane.
In other words, only the solvent or water may pass through such membrane, the solute or the dissolved substance in the water cannot pass through it. The parchment paper, egg membrane, goat bladder, etc., are the good examples of semipermeable membranes.
In the plant cell, the cell wall is permeable whereas the protoplasmic membrane is semipermeable. When concentrated and dilute solutions or the solutions of lower density and higher density are separated from each other by such membrane, then the solvent moves from a concentrated solution to dilute solution. This process is called the ‘osmosis’.
In other words, diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane is called osmosis.
The diffusion of water molecules continues to occur across the membrane till an equilibrium is acquired. At equilibrium water potential (Ψw)on both sides of membrane is equal.
To demonstrate osmosis experimentally following experiments may be done:
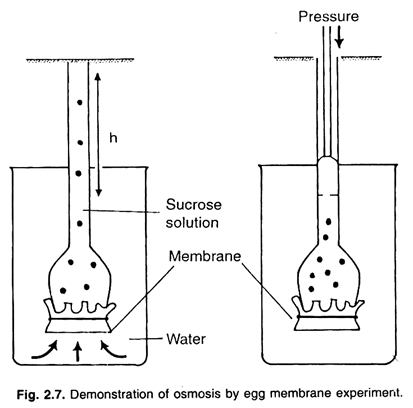
a. Egg Membrane Experiment:
To demonstrate osmosis by this experiment an egg is taken. On the pointed side of the egg a small hole is formed and all the white and yellow matter of the egg is taken out through this hole. Now the empty egg is placed in the dilute solution of hydrochloric acid (HCl), so that the hard shell of the egg constituted of calcium carbonate is dissolved in it. The membrane of the egg, found just beneath the cell remains intact.
Now this egg membrane is thoroughly washed with tap water, and a glass tube is inserted in it through its hole and tied tightly with a piece of thread, so that the end of the glass tube remains inside the egg membrane. Now, the concentrated solution of sugar is poured in it through glass tube with the help of a thistle funnel.
The sugar solution is filled up in such a quantity, so that after completely filling the egg membrane sac, it also reaches to a small height in the glass tube. Now this sugar solution filled egg membrane sac, is hanged in a beaker filled up with water, so that the level of the inner and outer liquid is same.
This apparatus is kept for some time in the same position. After some time it is to be noted that the level of the liquid inside the glass tube has sufficiently risen up from the level of the water of the beaker. Water will continue to move across the membrane, resulting in the rise of solution in the funnel until equilibrium is reached.
Pressure can be applied to the solution from upper part of funnel to prevent movement of water into it through egg membrane.
The pressure required to stop the movement of water completely is called osmotic pressure. This may be also referred as osmotic potential or solute potential
Osmotic pressure and osmotic potential are numerically equal, but osmotic potential has a negative (─) sign.
An isolated solution without solute, and not bounded by any membrane, has no osmotic pressure. It has only the potential to result into a pressure when placed in an osmometer.
Thus, a solution has an osmotic potential (Ψs), which is negative (─) of osmotic pressure (π, pi). The equation is Ψs = –π
If one reverses experiment by filling up the water in the egg membrane sac and the sugar solution in the beaker then the water moves from inner side to outer side. This process is called reverse osmosis. The process of reverse osmosis is used for removing salts from saline water.
Process of osmosis is controlled by two important factors:
i. Concentration of dissolved solutes in a solution, and
ii. Pressure difference.
These two factors determine the chemical potential of water, which acts as driving force for water movement in plants.
Water moves from a region of high chemical potential of water to a region of low chemical potential of water.
Chemical potential of water is also called water potential, and denotes free energy associated with water.
b. Potato Osmoscope Experiment:
One peeled potato tuber is taken. Now make it flat at its one end. Also make a deep and broad cavity on the other end of it, so that the bed of the cavity may reach up to flat surface, and the outer walls of the cavity become somewhat thin. Now fill up this cavity with concentrated sugar solution and place this potato osmoscope in a beaker containing water, so that the level of the outer and inner liquids may remain the same.
After a short time, it is to be noted that the level of the liquid filled in the cavity of the potato osmoscope goes higher, because of endosmosis. The density of the sugar solution, filled up inside the potato cavity is higher than the water of the beaker. Here, the tissues of the tuber act as a semipermeable membrane, and thus the water moves from outside to inner side.