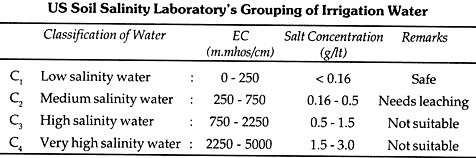
In this article we will discuss about the thallus and cell structure of oedogonium with the help of suitable diagrams.
Thallus Structure of Oedogonium:
The thallus is made of green, multicellular, un-branched filaments.
The filament is made of three types of cells (Fig. 1):
(i) The lower-most basal cell or holdfast.
(ii) The intercalary cells.
(iii) The upper-most apical cell.
(i) Hold Fast:
The filament is attached by means of specially differentiated basal cell. The holdfast is found in aquatic species and it rarely occurs in terrestrial forms. In terrestrial forms it may give out rhizoid like outgrowths. The hold fast or basal cell is club shaped, broad, round in upper part and narrow in lower part.
The lower terminal part of basal cells is multi-lobed, disc like or finger shaped which attaches the filament to substratum. Chloroplasts are absent or poorly developed in basal cell hence it does not take part in photosynthesis.
(ii) Intercalary Cells:
All cells of the filament in between apical cell and the basal cell are intercalary cells. The intercalary cells of filaments have base-apex polarity and this is maintained even when filaments break and become free floating. All intercalary cells are alike, only some cells after division develop cap in upper part. Such cells are called cap cells.
(iii) Apical Cell:
The terminal cell of the filament called apical cell. It is round or dome shaped. In some species e.g., O. ciliata, the apical cell is tapering and gives rise to narrow hair like structure. The apical cell is green due to chlorophyll and takes part in photosynthesis.
Cell Structure of Oedogonium:
The cells are elongated and cylindrical. The cell wall is generally thick, rough and rigid. It is made up of three concentric layers, the inner cellulose, middle pectose and the outer layer is chitinous in nature. The protoplasm consists of thin plasma membrane, cytoplasm, central vacuole, reticulate chloroplast and the nucleus.
The centre of the cell is occupied by a large central vacuole which contains the cell sap. The cell sap contains excretions, secretions and inorganic compounds. The protoplast occurs as thin layer between the central vacuole and the inner cell wall.
The chloroplast is characteristically reticulate, extending or covering the whole cell and encircling the protoplast (Fig. 2 A, B). The strands of reticulum may be broad or narrow depending upon the species. In most of the cases the strands are parallel to the long axis of the cell. Many pyrenoids are present at the intersections of the reticulum, Pyrenoids are covered with starch plates.
There is single large nucleus, it is biscuit shaped or biconvex and lies in the centre of cell, internal to the chloroplast. The nucleus possesses 1-2 nucleoli, and thread like or elongated chromosomes. The cell also contains mitochondria, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum and the other cell organelles.