In this article we will discuss about the asexual and sexual reproductive structure of volvox.
Asexual Reproduction of Volvox:
Study the slide of daughter colonies:
1. Asexual reproduction is with the help of daughter colonies which develop in parent colony.
2 Daughter colonies are present in the posterior side of the colony and formed by various divisions in some of the cells.
3. The number of daughter colonies in a parent colony varies from a few to as many as twenty.
4. Daughter colonies move for some time within parent colony.
5. Daughter colonies come out by rupturing the parent colony and behave as individual colonies.
Sexual Reproduction of Volvox:
Study the slides of sex organs:
I. Sexual reproduction is oogamous and coenobia may be homothallic or heterothallic.
2 Homothallic species are always protandrous, i.e., antheridia develop first and oogonia later on.
3. Sex organs are present in the posterior half of the coenobium.
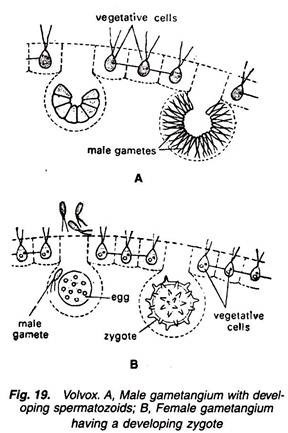
4. Antherozoids (Fig. 18) are formed in an enlarged cell (male gametangium), the contents of which divide into 32 to 256 parts.
5. Egg is present singly in female gametangium or oogonium which remains undivided.
6. Zygote is formed after fertilization, which takes place in the presence of water.
7. Zygote (Fig. 19) is surrounded by a three-layered smooth or spiny wall. It contains an orange-red pigment called haematochrome.