The reconstitution of ribosomes has been a dramatic advance of recent times. When ribosomes are centrifuged in a gradient of 5M CsCl, about 30 to 40% of the protein is lost. Both the subunits dissociated into 2 inactive core particles which contain the RNA and some proteins (core proteins).
Simultaneously some other proteins called split proteins (SP) are released from the ribosomes. When the split proteins are added to their corresponding core particles the ribosome is reconstituted.
The reconstitution of a functional 30S subunit has been achieved by the addition of 16S rRNA to a mixture of proteins from the 30S subunit. Following a similar procedure the 50S subunit has also been reconstituted. Along with the subunits the whole ribosome is also assembled.
When the 30S subunit is treated with 4M urea and 2M lithium chloride it dissociates and releases all the proteins. The 16S rRNA can be extracted from the 30S subunit by phenol. If now the 16S RNA is put together with the 2 proteins of the same subunit, reconstitution takes place.
Ribosomal RNA constitutes about 80-90% of the total cellular RNA. Due to high RNA content, ribosomes present in the cell cytoplasm stain with basic dyes such as toluidine blue.
For producing rRNA in such large quantities, the genes for rRNA are repeated a few hundred times in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In eukaryotes the genes for rRNA are transcribed in the nucleolus by RNA polymerase I; only the 5S rRNA present in the larger subunit is transcribed by RNA polymerase III.
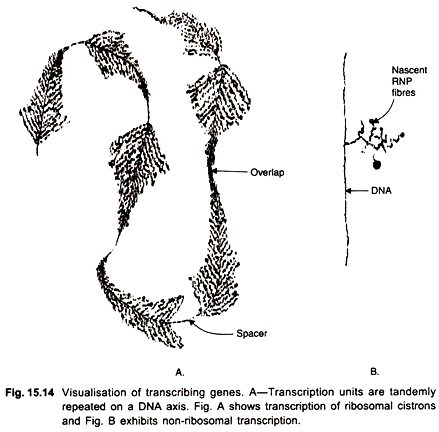
When transcription of ribosomal cistrons is observed in EM, the nascent transcripts are seen to be present in increasing length from the site of initiation to termination (Fig. 15.14); they are called Christmas trees. Two successive Christmas trees are separated by non-transcribed spacer segments. The primary transcripts become methylated to produce mature rRNAs; the spacers are degraded.
The synthesis of rRNA and the assembly of ribosomes take place in the nucleolus. The proteins of ribosomes are synthesized on the cytoplasmic ribosomes from where they pass into the nucleolus and become associated with rRNA.
In higher eukaryotes the genes for rRNA are clustered in the nucleolus organising regions of a few specific chromosomes. This region is recognised by the presence of a secondary constriction at metaphase. Mouse has six such chromosomes, whereas man and chimpanzee have five.
Each cluster means one transcription unit and there could be 40-50 units in a nucleolus organizer region. In Xenopus laevis and D. melanogaster the rRNA genes are present in a single cluster.
A mutant in X. laevis does not have a nucleolus (anucleolate mutant). In animals homozygous for this mutation there is no synthesis of 18S and 28S rRNA. The bobbed mutants in D. melanogaster are deficient in a portion of X chromosome which has genes for rRNA.