The below mentioned article provides a short note on the Cancer:- 1. Introduction to Cancer 2. Biochemical Laboratory Tests for Cancer 3. Clinical Orientation.
Introduction to Cancer:
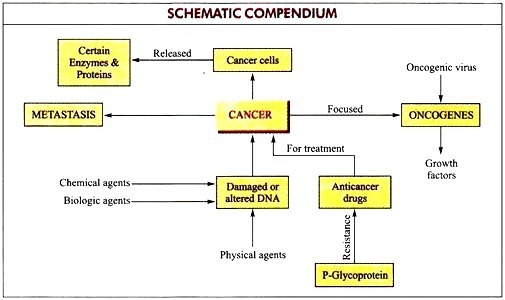
i. Cancer cells have the following characteristic properties.
(a) They have diminished control of growth.
(b) They invade local tissues.
(c) They spread to other parts of the body.
ii. The main object is to explain in biochemical terms the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells and their capacity to invade and metastasize.
iii. The genes controlling growth and interactions with other normal cells are apparently abnormal in structure or regulation in cancer cells.
iv. Information regarding the control of cell growth (both normal and pathologic) is limited and knowledge of specific genes involved in growth regulation is even very scanty. Little is also known as yet about the biochemical basis of metastasis.
v. Some types of cancer (e.g., certain leukemia’s) can be regarded as examples of abnormal differentiation. But little is known about the molecular basis of differentiation. Many workers in this area think that further research on oncogenes and growth factors will provide information on the nature of the disturbed control of growth, of differentiation, and of cell- cell interaction exhibited by cancer cells.
Biochemical Laboratory Tests for Cancer:
Many cancers are associated with the abnormal production of enzymes, proteins and hormones which can be measured in plasma or serum. These molecules are known as tumor markers. Measurement of some tumor markers is helpful in managing some types of cancer. The tumor markers are applied in diagnosis and management of cancer.
Three major conclusions are derived from the study of tumor markers:
i. No single marker is useful for all types of cancer or for all patients with a given type of cancer.
ii. Markers are most often detected in advanced stages of cancer rather than early stages.
iii. The most successful use of markers is to monitor the responses to therapy and the detection of early recurrence.
Clinical Orientation of Cancer:
i. After cardiovascular disease, cancer is the second most common cause of death in the world.
ii. Humans of all ages are victimized by cancer and different organs are affected by it.
iii. Many cancers are related to the increase of age ; the development of this disease is directly associated with the longer life.
iv. Proper treatment by surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapeutic agents in early stages of the disease can control the spreading of it. Otherwise, metastasis can develop rapidly with acute and uncurable symptoms causing death in the long run.