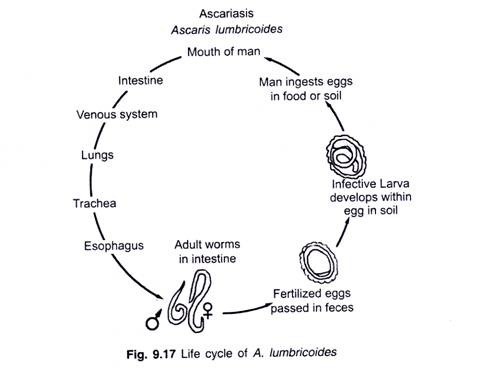
This article throws light upon the top five examples of flavone. The examples are: 1. Luteolin 2. Apigenin 3. Tangerine 4. Diosmin 5. Flavoxate.
Flavone Example # 1. Luteolin:
Luteolin is a flavonoid, more specifically it is one of the commonly available flavones.
Functions:
i. Play an important role in the human body as an antioxidant.
ii. A free radical scavenger.
iii. An agent in the prevention of inflammation.
iv. A promoter of carbohydrate metabolism.
v. An immune system modulator.
vi. Play an important part in the prevention of cancer.
vii. It can dramatically reduce inflammation and the symptoms of septic shock.
Occurrence:
Luteolin is most often found in leaves, but it is also seen in rinds, barks, clover blossom and ragweed pollen. It has also been isolated from Salvia tomentos.
Flavone Example # 2. Apigenin:
Apigenin is a flavone that is the aglycone of apiin, isolated from parsley and celery, and apigetrin. It is a yellow crystalline solid that has been used to dye wool.
Function:
Inhibition of adenylate cyclase and decreased the platelet cyclic AMP response to prostacyclin (Nikaidou et al., 2005). Tangeritin is a poly-methoxylated flavone.
Flavone Example # 3. Tangerine:
Tangerine, citrus peels, commercially available as a dietary supplement.
Functions:
i. Strengthens the cell wall and protects it from invasion.
ii. Cholesterol lowering agent.
iii. Potential protective effect against Parkinson’s disease.
iv. Potential as an anti-cancer agent.
v. In vitro studies showed anti-mutagenic, anti- invasive, and anti-proliferative effects.
Flavone Example # 4. Diosmin:
Diosmin is a semisynthetic phlebotropic drug, a member of the flavonoid family.
Functions:
i. It is used with Hesperidin to control internal symptoms of hemorrhoids (piles).
ii. It is an oral phlebotropic drug used in the treatment of venous disease, i.e. chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and hemorrhoidal disease (HD), in acute or chronic hemorrhoids, in place of rubber-band ligatino, in combination with fiber supplement, or as an adjuvant therapy to hemorrhoidectomy, in order to reduce secondary bleeding.
iii. Diosmin prolongs the vasoconstrictor effect of noradrenaline on the vein wall, increasing venous tone, and therefore reducing venous capacitance, distensibility, and stasis. This increases the venous return and reduces venous hyper pressure present in patients suffering from CVI.
iv. Diosmin improves lymphatic drainage by increasing the frequency and intensity of lymphatic contractions, and by increasing the total number of functional lymphatic capillaries. Furthermore, Diosmin (with Hesperidine) decreases the diameter of lymphatic capillaries and the intra-lymphatic pressure.
v. At the microcirculation level, Diosmin reduces capillary hyper-permeability and increases capillary resistance by protecting the microcirculation from damaging processes.
vi. Diosmin reduces the expression of endothelial adhesion molecules (ICAM1, VCAM1), and inhibits the adhesion, migration, and activation of leukocytes at the capillary level. This leads to a reduction in the release of inflammatory mediators, principally oxygen free radicals and prostaglandins (PGE2, PGF2a).
Flavone Example # 5. Flavoxate:
Flavoxate is a semisynthetic drug, a member of the flavonoid family having anticholinergic with anti-muscarinic effects.
Functions:
i. Muscle relaxant properties may be due to direct action on the smooth muscle rather than by antagonizing muscarinic receptors.
ii. Used to treat urinary bladder spasms.
iii. Flavoxate HCI is indicated for symptomatic relief of intestinal cystitis, dysuria, urgency, nocturia, suprapubic pain, frequency and incontinence as may occur in cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, urethrocystitis, urethrotrigonitis.
Adverse Reactions:
The following adverse reactions have been observed; but there are not enough data to support an estimate of their frequency.
Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth vertigo,headache, mental confusion, especially in the elderly, drowsiness, nervousness, tachycardia and palpitation, urticaria and other dermatoses, eoslnophilia and hyperpyrexia, increased ocular tension, blurred vision, disturbance in eye accommodation and dysuria.
Contraindications:
Flavoxate HCl is contraindicated in patients who have any of the following obstructive conditions: pyloric or duodenal obstruction, obstructive intestinal lesions or ileus, achalasia, gastrointestinal hemorrhage and obstructive uropathies of the lower urinary tract.