There are many useful application of microbes in the food industry. They influence the quality, availability and quantity of food. Microorganisms are used to change one substance to another which is used as food, such as milk to yoghurt and cheese, sugar to wine and bread.
Fermented Dairy Products:
Fermented milk is produced by inoculating pasteurised milk with specific culture of microorganisms. The different fermented dairy products include yoghurt and cheese.
Bacteria is used in Yoghurt Making:
Yoghurt is a dairy product which is produced by the bacterial fermentation of milk. Most commonly, cow’s milk is used, though it can be made from any kind of milk. It can be prepared from a variety of milk including whole, skimmed, dried, evaporated or semi-skimmed milk.
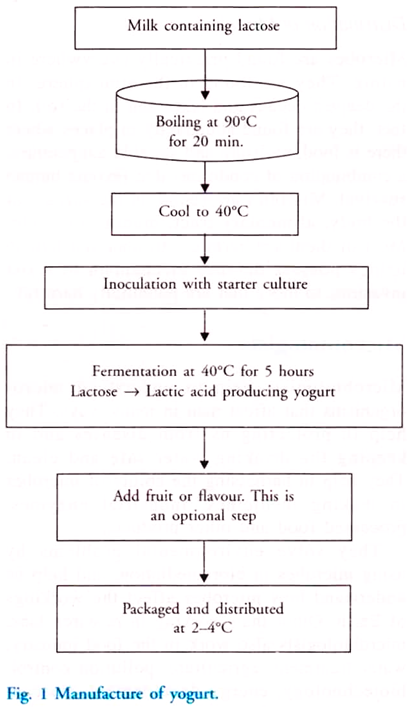
The steps involved in yoghurt making are illustrated in Fig. 1:
The milk sugar, i.e. lactose is fermented into lactic acid by the friendly bacteria, Streptococcus salivarius, S. thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. These bacteria are collectively known as lactic acid bacteria or LAB. The bacteria feed on the lactose and release lactic acid as a waste product.
The acid cause the curdling of the milk protein, casein into a solid mass called curd. The gel like texture and taste of yoghurt is due to the fermentation of lactose to lactic acid. The increased acidity (pH = 4-5) also prevents the proliferation of other potentially pathogenic bacteria.
Both unpasteurised and pasteurized milk may be used for yoghurt making. The use of unpasteurised milk maintains the healthy balance of bacteria and enzymes of milk in its unprocessed state under very carefully controlled temperature and environmental conditions. To ensure complete fermentation two or more different bacteria may be used together.
Yoghurt is often sold sweetened and flavoured, or with fruit added at the bottom. The flavour varies in different countries.
a. Lassi is yoghurt-based beverage in India and is consumed either salty or sweet. Salty lassi is usually flavoured with ground- roasted cumin and black pepper powder, while the sweet variety is served with lemon, mango or other fruit juice.
b. A lassi-like, salty drink called ayran is popular in Turkey and Bulgaria and is prepared by mixing yoghurt with water and salt.
In India, Bulgaria and Turkey yogurt is prepared at home using a small amount of plain active culture yogurt as the starter culture. The milk is boiled to kill undesirable microbes. It is cooled to about 40°C. A tablespoon of starter culture is added and mixed thoroughly. It is left undisturbed for about 6 hours.
Bacteria and Fungi are used in Cheese Making:
Cheese is prepared by inoculating milk with a starter culture containing specific microorganisms. Cheese is a solid food made from the milk of various animals, most commonly cows. Milk from goat, sheep, reindeer and water buffalo may also be used. There are several types of cheese.
Fermentation of milk leads to lactic acid production, which sours the milk. This leads to coagulation of milk protein, casein. The solid part of the milk produced by coagulation is known as curd and the liquid is known as whey.
The curds can be separated and pressed into desired shape and whey is used as food source for yeasts, which in turn can be processed as cattle feed and is rich in protein and vitamins. The cheese can be matured or ripened by the addition of bacteria or fungi or both. The bacteria added reduce the pH, alters texture and develops a flavour.
Coagulation can be controlled using rennet tablets, which contains the enzyme rennin. Rennin is an enzyme present in the stomach of Calves but now is also available in genetically engineered bacteria. Coagulation can also be done using acids such as vinegar or lemon juice.
Depending on the nature of the organism added, cheese is of the following types:
a. Cheddar cheese is prepared by the addition of bacteria to enhance its flavour and texture.
b. The use of mould fungi produces Roquefort cheese and blue cheese
c. A combination of both bacteria and fungi produces camembert cheese.
d. Swiss cheese is prepared by the addition of Propionibacterium sharmanii. The big holes in the cheese is because of the production of large amounts of CO2.
The natural colour of cheese ranges from off-white to yellow. Herbs and spices may also be added to the cheese. Other factors that contribute to a different flavours and styles of cheese are different levels of milk fat, variations in length of aging, different processing treatments and different breeds of cows, sheep or other mammals.
Table 3 summarises the major classes of cheese:
Cheese is sold in the form as slices or in blocks or as a thick fluid. In addition, there is a class of cheese known as processed cheese or cheese food. Processed cheese is similar to cheese, but contains emulsifying salts acting as stabilisers. Heat treatment during the manufacturing process gives processed cheese a mild flavour.
Other Fermented Foods:
Some important food produced in whole or in part by microbial fermentation are pickles, sausages, etc. Different microorganisms are added to specific stages of food production to produce the desired effect. Moulds are used for the fermentation of rice to produce a variety of oriental foods.
Yeast is used for Making Bread:
Yeast is a fungus that feeds saprotrophically. The enzymes secreted by the yeast cell, digest food that contains sugar and minerals. Yeast is used to make bread. When yeast is added to raising flour and water, carbon dioxide is produced which gets trapped in the dough prepared from the flour.
The dough rises and bread is made. The flour is usually made from wheat and contains starch. Starch is the energy source for the yeast. The flour also contains a protein called gluten, which forms sticky stretchy threads as the yeast works on the sugar. The threads trap the carbon dioxide and make the dough rise well.
Some commercial uses of yeast are shown in Table 4:
Baker’s Yeast:
Yeast is used as leavening agent in baking since earlier times. The most commonly used species is Saccharomyces cerevisiae because of its ability to ferment sugar in the dough vigorously and to grow rapidly. The carbon dioxide used during the fermentation is responsible for the leavening or the rising of the dough. The procedure of mass production of Baker’s yeast is elaborate under controlled conditions of pH, temperature conditions.
Microorganisms as Food – Single Cell Protein:
Algae, yeasts and bacteria can be grown in large quantities to yield a cell crop which is rich in protein known as single cell protein. The protein may be used for human consumption or as animal feed. It may be a useful source of minerals, vitamins, fat and carbohydrates. The composition of the different SCP depends upon the organism and the substrate on which it grows.
The advantages of using microorganisms as a food source are:
a. They grow very fast and do not need much space as conventional crops.
b. They grow on a wide range of cheap, waste products of agriculture and industry such as petroleum products, methanol, ethanol, sugar, molasses, waste from paper mills etc. The secondary advantage is that they help in recycling the materials and thereby clean up the wastes.
c. They are high yielding. In a growth medium of 1000 lb of yeast in one day, many tonnes of protein is produced. This is about 10-15 times greater than soyabean and about 25-50 times greater than corn.
d. The protein content of the cells is very high. Yeast cells have a protein content as high as 40-50%; for algae the range is 20- 40%.
e. The proteins of the microorganism contain all the essential amino acids.
f. Some microorganisms, particularly yeasts, have high vitamin content.
g. Factors, such as climate do not affect them, since they do not occupy large areas of land.
Pruteen was the first major SCP to be produced. It was produced by a bacterium, Methylophilus methylotrophus. Methanol was used as a source of energy and the temperature was maintained at 30-40°C and pH at 6.7.
Pruteen was rich in essential amino acids and has high vitamin content. It is twice as nutritious as soyabean meal and was used as an animal feed.
Some disadvantages of using SCP:
a. The high nucleic acid content causes intestinal disturbances. It can also lead to an increase in the uric acid in the blood that will eventually lead to gout. Additional processing can be done to reduce the nucleic acid content, but this would increase the cost.
b. Bacterial cells have small size and low density, which makes harvesting from the fermented medium difficult and costly.
c. The taste is not acceptable for many persons. Individual taste and customs make microorganism unattractive as a food to some individuals.
Chocolate Making:
Chocolate is prepared with the help of microbes. Chocolate comes from the seeds of cacao trees. These seeds are found in a white fleshy pod. To remove the seeds out of the pod, the pod is allowed to ferment with naturally occurring microbes that include yeasts and bacteria such as Lactobacilli and Acetobacter.