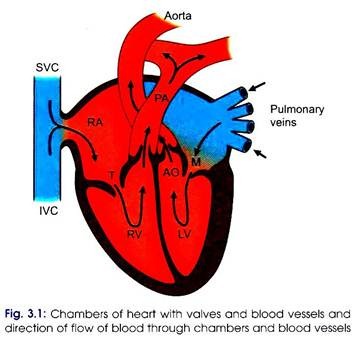
Cardiovascular system deals with study of heart and blood vessels. The human heart is made up 4 chambers namely; 2 atria and 2 ventricles. Atria are thin-walled chambers. Right atrium receives venous blood from peripheral parts of body. The venous blood is brought to right atrium by superior and inferior vena cavae.
Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from lungs. This blood is brought to left atrium by pulmonary veins. The two atria also act as weak pumps and blood is pumped from right and left atria into right and left ventricles, respectively (Fig. 3.1).
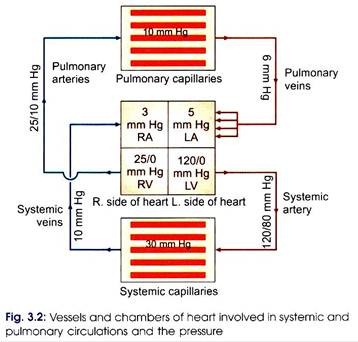
Comparatively, ventricular walls are thicker than the atrial walls. Right ventricle is less thick-walled than the left ventricle. The ventricles act as primary pumps. From the right ventricle, blood is pumped into pulmonary circulation and from the left ventricle blood is pumped into systemic circulation (Fig. 3.2). Volume of blood pumped out by the right or the left ventricle every minute is the cardiac output.
Normal cardiac output is about 5 liters per minute.
Blood Vessels:
The systemic circulation starts with aorta. Aorta acts as a damping vessel. Aortic wall contains plenty of collagen and elastic fibers. Collagen fibers prevent rupture of the vessel. The elastic fibers are stretched when blood enters aorta from left ventricle during ventricular systole (contraction of ventricle).
Blood that enters aorta during ventricular systole is accommodated due to the stretching of elastic fibers. During ventricular diastole (relaxation of ventricle), the accommodated blood in aorta is made to flow towards periphery due to the recoiling of the elastic fibers. It is because of this, aorta acts as a secondary pump.
Blood that enters systemic circulation supplies oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and at the same time it removes carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes from tissues. Systemic circulation is a high pressure area. The pressure will be around 120/80 mm Hg.
Venous blood that has entered right ventricle is pumped into pulmonary artery. This blood takes part in exchange of gases at lungs. Because of this, oxygen from lung diffuses into blood and at the same time carbon dioxide is diffuses from blood into alveolar air. The oxygenated blood is returned to left side of heart by pulmonary vein. The pulmonary circulation is a low pressure area and the pressure will be around 25/10 mm Hg.