The below mentioned article provides study notes on Translocation of Peptides.
The synthesis of peptides in the ER through signed sequence has been described. There are several types of processes for the transfer of peptides into and through membranes in the ER, mitochondria etc. Generally, peptides with cleared or un-cleared signal sequence are transported into these membranes.
There are differences in the composition of the signal recognition particle (SRP), receptor of the SRP and in the maturation process of the peptides.
When the signal sequences are in the interior of the peptide molecule and not at the N terminal portion of the peptide, they act as stop-transfer signals. In other words, peptide molecules will not pass through ER. The transport of peptides takes place along with its translation, so it is called co-translation process.
The transport of the peptide may take place either after cleavage of the terminal signal sequence or the peptides may enter into the two domains, i.e., in the cytoplasm and in the lumen of ER with the cleavage of signal sequence. The signal sequence remains bound to the membrane.
Cleavage of Signal Sequence:
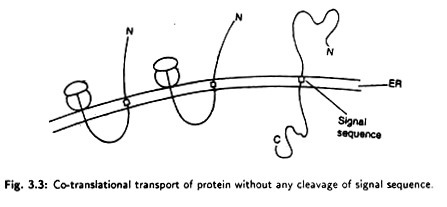
Cytochrome b5, Calcium transferring ATPase and some plasma membrane proteins are transported through the membrane without any cleavage of the signal sequence (Fig. 3.3).
 The uptake of proteins into mitochondria and chloroplasts takes place in a special way. Most of the proteins of these organelles are synthesised on the ribosomes of the cytoplasm and then transported to the organelles.
The uptake of proteins into mitochondria and chloroplasts takes place in a special way. Most of the proteins of these organelles are synthesised on the ribosomes of the cytoplasm and then transported to the organelles.
Co-translational transport, i.e., simultaneous synthesis and uptake of protein/peptide into the membrane, do not occur in these organelles like that of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. In case of these organelles, proteins are first synthesised on the cytoplasm and then these are bound to the outer membrane by a membrane receptor for transportation.
These proteins are then distributed to the outer membrane, inner membrane and the matrix of the mitochondria. At first, proteins are synthesised in the cytoplasm, then a 40 KD protein is attached with the signal sequence present at the N terminal portion.
This 40 KD protein helps to identify the receptor protein present in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Finally, with heads protruding out of proteins, they are distributed to the different areas of the mitochondria with the cleavage of signal sequence.