For the first time, yeasts were observed and reported by Leeuwenhoek (1680).
First of all reported yeasts. Yeasts are nonmycelial (unicellular) saprotrophic ascomycetes. They are cosmopolitan in distribution that grows in sugar rich medium, milk, on sweet fruits, decaying vegetables and some on animal excreta.
They are of 2 types:
(a) True yeasts (ascosporic yeasts):
Develop ascospores inside asci or ascocarps. They include 68 species belong to 14 genera, e.g., Sacchuromyces, Zygosaccharomyypces. Schizosaccharomyces, Nodosonia. Pichia etc.
(b) False yeasts (asporogencus yeasts):
Similar to true yeasts but don’t form spores or asci. They are included under deuteromycetes (fungi imperfecti), e.g. Candida, Mycoderma etc.
Kinds of yeast:
On the basis of asexual or vegetative reproduction yeasts are of 3 types:
(a) Budding yeast: e.g. Saccliaromyes cerevisiae. (known as both baker’s yeast as well as Brewer’s yeast)
(b) Fission yeast: e.g. Schizosaccharomyces octosporus
(c) Helobial yeast: Reproduce by both budding and fission, e.g. Saccharomycodes ludwigii.
Economic Importance of yeasts:
Useful activities:
1. Baking industry’:
In bread preparation. S. cerevisiae is added to the needed flour. Fermentation activity of yeast produces alcohol of CO2. The CO2 evaporate and makes the bread spongy.
2. Brewing industry:
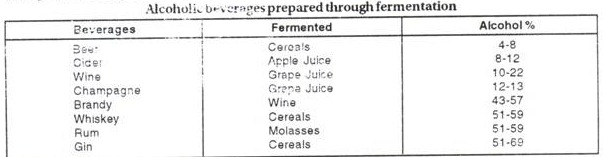
S. cerevisiae (brewer’s yeast) and S. ellipsoidens (wine yeast) perform alcoholic fermentation in a large fermentor or bioreactor. This froms a variety of alcoholic beverages like beer, wine, brandy, cider, Champagne etc. All of them differ in ethanol percentage. Ethanol used as solvent, liquid fuel (gasohol) and antifreeze.
3. Yeast cake:
In brewing industry, excess yeasts are harvested and pressed into yeast cakes or tablets which are a rich source of proteins and vitamins (B1, B2 and C).
Harmful activities:
(i) Spoilage of food:
Due to saprotrophic nature yeast spoil a number of food stuffs like cheese, tomato products, carbonated beverages, food with lactic acid etc.
(ii) Plant diseases:
Nematospora attack beans, tomato and cotton and reduce their yield.
(iii) Human diseases:
Some species of yeasts are responsible for serious diseases like cryotococcosis (amental disorder), blastomycosis, torulosis, histoplasmosis, candidiasis etc.