Read this article to learn about the phytochemicals for arthritis and its separation strategies.
The major compound types of anti-rheumatism agents in herbs usually involve phenolic, stilbene and polyphenol compounds, flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids anthraquinones, lignans polysaccharides and peptides. Some chemical entities for Arthritis are presented, in Table 17.2.
These compounds may also be antibacterial. For the analysis of plant medicines, chromatographic techniques (TLC, CC, SFC, HPLC and HPTLC) are frequently used methods and act as standards for identification and quality control of the most herbal medicines as illustrated in pharmacopoeia of different countries. Structures of some anti-arthritic leads are shown in Figure 17.1.
In anti-rheumatism plant medicines, terpenoids are the most typical kind of volatile active components.
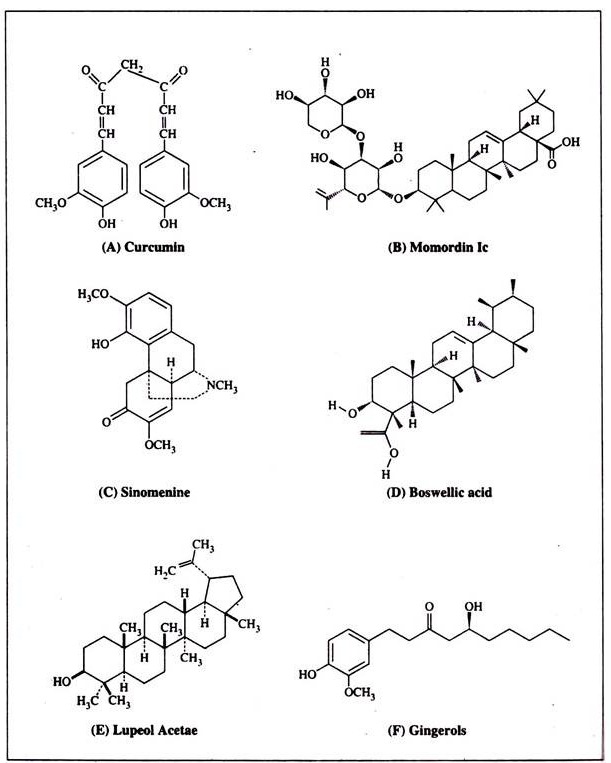
 Kutney et al (1992) isolated various metabolites of interest in rheumatoid arthritis from Trip-terigium wilfordii. Triterpenoids, terpenoids etc. has also been isolated from this particular plant.
Kutney et al (1992) isolated various metabolites of interest in rheumatoid arthritis from Trip-terigium wilfordii. Triterpenoids, terpenoids etc. has also been isolated from this particular plant.
Column Chromatographic fractionation of petroleum ether extract of Strobilanthus with petroleum ether and benzene (65: 35) yielded lupeol and 19a-H lupeol and was simultaneously evaluated for its anti-arthritic effect.
Apocyanin, 1-(4- hydroxy-3-methoxy phenyl)-ethanone, is a plant derived drug discovered during activity-guided isolation of immunomodulatory constituents from Picrorhiza kurroa. Apocyanin is found to be inhibitory in inflammation mediated cartilage destruction and also decreases IL-1 and TNF-∝ production.
MomordinIc and its aglycone, oleanolic acid, isolated from Kochia scoparia fruits could be the active principles for rheumatoid arthritis. From the fraction of BuOh extract of Kochia scoparia in column chromatography, eluent CHCl3-MeOH-H2O (65:35:10), crystal of momordin Ic was obtained.
Isolation of acid hydrolysed from the same plant afforded oleanolic acid (Momordin lb, 3) and its 6′-0-methyl ester (2). Subramanian Sethi (1969) isolated withaferin A from with- iana cougulans roots. The same was studied for anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity in the same laboratory.
It was concluded that Withaferin A, to be more potent than hydrocortisone, standard, in adjuvant induced arthritis in rats. The root of Zizyphus vulgaris is ethnomedicinallly used in gout and rheumatism, Mukhtar et al, 2005 has isolated Ursane-Type triterpenes taking C&H6-CHCl3 (3:1) as eluant.
However this particular compound was not evaluated for the activity. Myricaria paniculata (Tamaricaceae) has been reported to cure arthritis in China. Li Shuai et al., 2004 isolated two new triterpenoids myricare A and B along with other previously reported phytochemicals from the stem.
Alpha and beta boswellic acids (BA) and re-related analogs were isolated from the ethanol extract of Boswellia carterii. 45 grams of etahnolic extract of B. carterii was chromatographed using 250 g silica gel column. The solvent consists a gradient solvent system consisting of n-hexane with increasing amounts of ethyl acetate. A total of 120 fractions (250 ml/fraction) were collected.
The fractions 33 through 68 and fractions 69-85 were sub purified by HPLC which yields acetyl- 11 – dien-beta-BA: acetyl-alpha-BA: acetyll -Beta- BA and alpha-BA; beta-BA respectively. Fractions 86 through 98 and fractions 99 through 118 were recrystallized without subpurification. AcetyI-11 – keto-beta-BA were obtained from fractions 86-98 and fractions 99-118 respectively.
