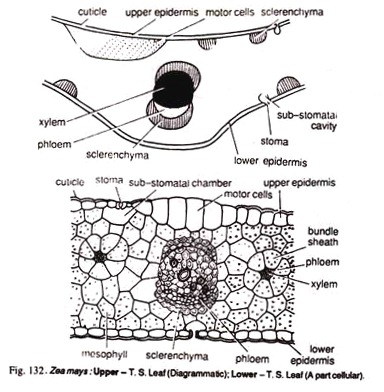
In this article we will discuss about the anatomy of Zea mays and Triticum monocot leaves.
1. Anatomy of Zea mays – Leaf (Family – Graminae):
T. S. reveals the following structures:
Epidermis:
1. A single layer is present on the upper as well as lower surfaces of the leaf.
2. Both the epidermal layers, i.e., upper as well as lower, contain stomata.
3. A thick cuticle is present on both the epidermal layers.
4. Some cells of upper epidermis are larger in size. These are called bulliform cells or motor cells.
Mesophyll:
5. In between the epidermal layers is present the region of chlorophyll containing cells called mesophyll.
6. It is not differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
7. The cells are spherical or angular with only a few or no intercellular spaces.
8. The cells of this region are arranged compactly.
Vascular bundles:
9. Many small and large bundles are present.
10. Vascular bundles are collateral and closed.
11. Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a layer of thin walled, parenchymatous cells called bundle sheath.
12. The cells of the bundle sheath contain starch and plastids.
13. On both the ends of large vascular bundles are present patches of sclerenchyma which extend upto the upper and lower epidermal layers.
14. In the large bundles, xylem and phloem elements are more visible than small bundles.
15. Xylem is present towards the upper epidermis and phloem towards the lower epidermis in the large vascular bundles.
16. Xylem consists of vessels, tracheid’s and xylem parenchyma.
17. Metaxylem is represented by two large oval vessels and the protoxylem by a water cavity called lysigenous cavity.
18. Phloem consists of sieve tubes and companion cells.
19. Smaller vascular bundles consist of less developed xylem and phloem surrounded by a bundle sheath.
Xerophytic Points:
(a) Presence of thick cuticle.
(b) Presence of patches of sclerenchyma.
(c) Presence of motor cells.
(d) Presence of stomata.
Identification:
(a) 1. Presence of expanded portion or blade.
2. Upper and lower epidermal layers are present.
3. Presence of mesophyll.
4. Presence of bundle sheath. (Leaf)
(b) 1. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly.
2. Absence, of cambium.
3. Presence of stomata on both the surfaces.
4. Vascular bundles are collateral and closed.
5. No differentiation of palisade and spongy parenchyma in mesophyll. (Isobilateral, monocot leaf)
2. Anatomy of Triticum – Leaf (Family – Graminae):
T. S. shows prominent ridges and grooves and reveals the following tissues:
Epidermis:
1. Two epidermal layers are present, one each on upper and lower surfaces.
2. Uniseriate upper and lower epidermal layers are composed of more or less oval cells.
3. Few big, motor or bulliform cells are present in groups here and there in the furrows of upper epidermis.
4. Stomata, each consisting of a pore, guard cells and a stomatal chamber, are present on both the epidermal layers.
5. A thick cuticle is present on the outer walls of epidermal cells.
6. Bulliform cells help folding of leaves.
MesophyII:
7. It is not clearly differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma but the cells just next to the epidermal layers are a bit longer while the cells of the central mesophyll region are oval and irregularly arranged.
8. The cells are filled with many chloroplasts.
9. Many intercellular spaces are also present in this region.
10. Sub-stomatal chambers of the stomata are also situated in this region.
Vascular System:
11. Many vascular bundles are present in the material, arranged in a parallel series.
12. The central vascular bundle is largest in size.
13. Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and closed.
14 Each vascular bundle remains surrounded by a double layered bundle sheath.
15. Outer layer of bundle sheath consists of thin walled cells while the inner layer is made up of thick walled cells.
16. On the upper as well as lower surfaces of large vascular bundles are present patches of sclerenchyma which are closely associated with the epidermal layers. There is no such association between the sclerenchyma and small vascular bundles.
17. Xylem occurs towards the upper surface and phloem towards to lower surface.
18. Xylem consists of vessels and tracheids. Sometimes small amount of xylem parenchyma is also present.
19. Phloem consists of sieve tubes and companion cells.
Xerophytic Points:
(i) Thick cuticle on epidermis.
(ii) Presence of motor cells.
(iii) Sclerenchyma patches are present.
(iv) Stomata in furrows.
Identification:
(a) 1. Presence of upper and lower epidermal layers.
2. Mesophyll is present.
3. Each vascular bundle is surrounded by bundle sheath. (Leaf)
(b) 1. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly.
2. Absence of cambium.
3. Vascular bundles are collateral and closed.
4. Stomata on both the surfaces. (Isobilateral monocot leaf)