There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves in man. They are numbered by Roman numeral I to XII. A cranial nerve arises from the brain by two roots, a dorsal and a ventral root.
These two roots do not unite but appear like separate nerves. The cranial nerves are generally medullated (having a myelin sheath).
The following table shows the origin, nature and distribution of cranial nerves:
The nerve fibres which carry impulses or sensations or stimuli are of 3 kinds. They are sensory, motor and mixed nerve fibres. The sensory or afferent nerve fibres carry impulses or sensations from the receptors like skin, eye, ear etc. to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
The motor or efferent nerve fibres carry impulses or sensations from the central nervous system to the effectors like muscles and glands. Certain nerves contain sensory and motor fibres, and hence are mixed type. All the body functions can be conveniently divided into two categories: somatic functions and visceral functions.
Somatic functions are performed by the help of the body wall (skin and muscles) and visceral functions are carried on by internal organs like the digestive, circulatory, urinogenital, and respiratory or endocrine glands. Accordingly the nervous system has four functional components and four kinds of nerves.
They are as follow:
(a) Somatic sensory nerves carry impulses from somatic receptors such as skin, eyes, nose, body walls and joins to central nervous system.
(b) Somatic motor nerves carry impulses from central nervous system to voluntary muscles.
(c) Visceral sensory nerves carry sensations from the viscera to the central nervous system.
(d) Visceral motor nerves carry impulses from the central nervous system to the involuntary muscles of alimentary canal, glands and other visceral organs.
Spinal Nerve:
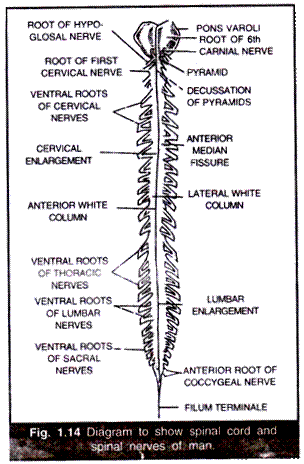
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves in man — arising in pairs from the spinal cord. Out of these 8 pairs are Cervical, 12 pairs Thoracic, 5 pairs Lumbar, 5 pairs Sacral and 1 pair Coccygeal nerve (Fig. 1.14 and 1.16).
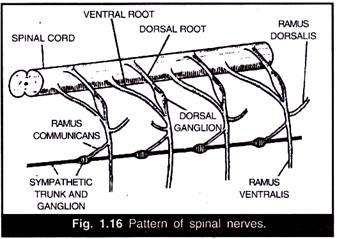
The spinal nerves are of mixed type and arise in pairs from the spinal cord by two roots, a dorsal root and a ventral root (Fig. 1.14 and 1.16). The dorsal or sensory root consists of afferent fibres which may be somatic sensory or visceral, sensory. It also bears a ganglion. The ventral root consists of efferent fibres which may be somatic motor or visceral motor fibres. These two roots unite to form a spinal nerve which comes out through a small aperture between vertebrae called inter-vertebral foramen guarded by a silvery- white calcareous gland known as glands of Swammerdam.
Soon after its emergence, the spinal nerve trunk divides immediately into three branches as follows:
(a) Ramus dorsalis contains somatic sensory fibres and supplies the skin and muscles of dorsal body wall.
(b) Ramus ventralis is the thick, main nerve and contains somatic motor fibres.
(c) Ramus communicans contains visceral sensory and visceral motor fibres and later joins autonomic nervous system and spinal cord.