This article throws light upon the top twenty two types of fruit crops in India. The fruit crops are: 1. Mango 2. Guava 3. Papaya 4. Pomegranate 5. Citrus 6. Banana 7. Litchi 8. Sapota 9. JackFruit 10. Aonla 11. Ber 12. Bael 13. Jamun 14. Pineapple 15. Apple 16. Peach 17. Pear 18. Plum 19. Grape 20. Coconut 21. Arecanut 22. Karonda.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 1. Mango:
1. A Mango is also known as King of fruits/ National fruit/ Bathroom fruit.
2. Botanical name: Magnifier indicia, Family: Anacardiaceous
3. Origin place: – South Asia / Indo-Burma region.
4. Major Producing States: Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Karnataka,Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Orissa and Maharashtra.
5. Botany: Fruit type – Berry
6. Edible part – Meso-carp
7. Mango fruit has the highest Vitamin A.
8. Mango is the highest largest producing and exporting fruit of India.
9. During 2008-09, mango has:
Area – 2309 (000′ HA) – highest in U.P.
Production -12750 (000′ MX) – highest in A.P.
Productivity – 5.5 (MT/HA)
9. Latest Production: 127.50 lakh tonnes
10. India’s shares about 57% of the total mango production in the world.
11. Mango production is > 40% of the total fruit production of India.
12. Propagation method:
Commercially propagation – Veneer grafting and Epicotyl grafting In situ propagation – Side grafting
13. Advanced Technology – High density planting (Amrapalli variety)
14. Planting distance of mango is 10 m ’10 m.
15. Cogging technique of breeding is used 1®’ time in mango by Dr. R.N. Singh.
16. Longevity of mango seeds is 30 days (4 weeks).
Commercial Mango Varieties Grown in Different States:
Mango Varieties and their Important Characteristics:
1. Alphanso – Most popular variety of India, highly export qualitab le, susceptible to spongy tissue.
2. Amrapali – High intensity variety (2.5 m’ 2.5 m). Dwarf, regular bearers, cluster bearing, small sized fruits, good keeping quality.
3. Ark Puente – Regular bearer, attractive skin colour and medium sized, free from spongy tissue, good keeping quality, good sugar acid blend.
4. Bombay green – Earliest variety of North India, Pollinizing variety, highest Vit. C, it is also called Malda in UP and Sehroli in Delhi.
5. Banganapalli – Main commercial var. of A.P.
6. Chousa – Sweetest variety.
7. Dashehari – Most popular variety of N. India.
8. Fazli – Late maturing variety.
9. Kesar – Good processing variety.
10. Langra-Most prone to fruit drop.
11. Lai sindhu – Powdery mildew resistant variety.
12. Mallika – Regular bearers, high TSS, good colour, uniform fruits,moderate keeping quality.
13. Niranjan – Off season bearer.
14. Neelum – Best combiner variety, ideal for long transportation, gives two crops in a year.
15. Ratna – Regular bearer, free from spongy tissue and fibre.
16. Rosica-Mutant variety.
17. Rumani – Apple shaped variety.
18. Sindhu – Seedless variety.
19. North Indian varieties are generally alternate bearer and mono embryonic, whereas South Indian varieties are generally Regular bearer and poly embryonic.
20. Regular bearer varieties are Ratna, Neelum, Himsagar, Gulab khas, Pairy, Totapari.
21. In India, 10 poly-embryonic varieties are found which are namely Olour, Goa, Salem, Bellary, Chandrakaran, Bappakoi, Kurkan, Nileshzvar dwarf, Solan and Mulgoa.
22. Self incompatible mango varieties are Dashehari, Langara, Chousa, Bombay green.
23. Hybrid varieties:
a. Mullica – Neel am x Dashehari (NDM)
b. Amrapalli – Dashehari x Neelam (DNA)
c. Ratna – Neelam x Alphanso (NAR)
d. Sindhu – Ratna x Alphanso (RAS)
e. Arka puniest – Alpha so x Baganapalli (ABaAp)
f. Ark arena – Baganapalli x Alpha so (BaAAa)
g. Ark Neelkiran – Alphas x Neelam (ANAn)
h. Manjeera – Rumani x Neelam (RNM)
24. New varieties released from l AR I:
(a) Pusa surya
(b) Pusa Arumina (Amrapalli’ Sensation)
(c) Akshay-selected from Dashehari
25. Only 0.1% flowers (perfect) develop into fruits to mature.
26. Number of perfect flower is found highest in Langra, whereas lowest in Rumani Variety.
27. Paclobutrazol (5-10 ppm) chemical is most commonly used for flower induction.
28. Housefly works as a pollinator for mango.
29. C: N ratio is 10:1.
Requirement of Major Nutrients in Different Ages:
1. Cluster in mango is known as Jhumka which is due to improper pollination.
2. Harvesting period – March to mid August.
3. Mangoes are highly susceptible to low temperature injury, that’s why they should be stored above 50c temperature.
4. Vapour heat treatment (VHT) is recommended for disinfection of mango against fruit flies.
5. Good mango variety has a 20% TSS.
6. Storage Conditions:
a. Temperature: 13oC
b. Relative Humidity: 85-90%
c. Storage period: 23 Weeks
d. Freezing point: 10C
7. Sensibility to: Refrigeration, Freezing and Ethylene exposure.
8. Disorders/ Diseases/ Pests:
a. Internal fruit necrosis – due to Boron deficiency
b. Sap burning – Post harvest disorders
c. Mango malformation – caused due to Fusarium moniliform, spray of NAA @ 200 ppm at the time of fruit bud differentiation.
d. Black tip – due to brick kiln fumes (contains SO,, CO, & CO), spray Borax (0.8%).
e. Mango mealy bug
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 2. Guava:
1. Guava is commonly known as “Apple of tropics”,
2. Botanical name: Sodium guajava L., Family: – Myrtaceae
3. Origin: – Tropical America
4. Season of planting: June-December.
5. Planting Space: 6 m x 6 m
6. Pit size: 60 cm x 60cm x 60 cm
7. Commercial Propagation method: Air layering.
8. Varieties: Lucknow- 46, Lucknow- 49 (Sardar), Allahabadi safeda, Chittidar, Apple colour, Seedles guava. Red guava, Nasik, Hafsi, Harijha, Arka Mridula, Lalit, Nagpur seedless and Allahabad round (Parthenocarpic var.) etc.
Hybrids: 1. Kohir safed: Kohir x AS (Allahabad Saphead) 2. Safe jam: AS X Kosher
Requirement of Major Nutrients in Different Ages:
9. Major pests are fruit fly, mealy bug, aphids etc.
10. Major infesting diseases are Red rust and wilt.
11. Harvest: Generally, Guava harvested throughout year except May and June. Layers come to bearing in 2 – 3 years. The first crop can be harvested during February – July and the second one during September – January.
12. Yield: The crop yields about 25 t/ha.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 3. Papaya:
1. Papaya is commonly known as “Melon tree”.
2. Botanical name: Carica papaya L., Family: Caricaceae
3. Origin: Tropical America
4. Yellow pigment in papaya: Caricaxanthin
5. Climate and Soil:
It is a tropical fruit and grows well in regions where summer temperature ranges from 35°C – 38°C. Tolerates frost and comes up to an elevation of 1200 m above mean sea level. Well drained soils of uniform texture are highly preferable to avoid the collar rot disease.
6. Sowing:
500 g of seeds is required for planting one ha. June-September is the best season for planting. Avoid planting in rainy season.
7. Nursery:
Treat the seeds with Captain @ 2 g/kg of seeds. Dibble four seeds in polythene bags in depth not exceeding one cm. keep the polythene bags in partial shade. Watering can be done with the help of rose can. Seedlings will be ready in about 60 days.
8. Planting:
Plant the seedlings in pits of 45 cm x 45 cm x 45 cm size.
9. Planting Space:
2m’2m (1.25’1.25 for Pusa Nanha)
10. Commercial Propagation method: Seed.
Seed rate/ha: 250-300 gm (Igm = 20 seeds)
15. Irrigation:
Irrigate copiously after planting. Irrigate the field once in a week.
11. Varieties:
Pusa nanha, Pusa majesty, Taiwan, Washington, Pusa delicious, CO- 1,2,3,4,5,6& 7, Coorg, Honey dew and Surya.
(a) For Table purpose – Co 3, Co 7 and Surya.
(b) For table + papain production – Co 2, Co 5 and Co 6.
(c) Gynodioecious (bisexual + female) – Pusa delicious, Pusa majesty, CO-3, Coorg honew dew. Sunrise solo, Taiwan, Surya.
(d) Didecious – Pusa dwarf, Pusa Nanha, Pusa giant, CO-1,2,5,6, Pant-C-1
(e) Suitable for high density planting (HDP) – Pusa Nanha
(f) Highest papain yielders – Pusa majesty, CO-5 etc.
(g) Hybrid: 1. CO-3: CO-2’Sunriseso/o
2. CO-4: CO-2 ‘ Washinghton
3. CO-7: CO-3 ‘ Pusa delicious ‘ Coorg honey dew
Requirement of Major Nutrients in Different Ages:
12. Flowering time: July-Sept.
13. Fruiting time: Feb-June:
14. Major pests are red spider and Papaya ring spot virus.
15. Major infesting disease is Damping off.
16. Harvest: Fruits should be picked at colour break stage.
17. Yield: 200-250 t/ha.
18. Papain extraction:
Papain has several industrial uses, the important one being in brewing industries. It is used as “meat tenderiser” and in textile and leather “sanforization” processes and drugs.
Method of Extraction of Papain from Papaya Fruit:
The latex should be tapped from immature papaya fruits. Select 75 to 90 days old fruits. On the selected fruit, give incisions (cut) with a razor blade or stainless steel knife. The cuts should be given from stalk to tip of the fruit.
The depth of the cut should not be more than 0.3 cm. Four such cuts are given spaced equally on the fruit surface. Tap the latex early in the morning and complete the tapping before 10.00 a.m. repeat the tapping four times on the same fruit at an interval of three days.
The cut should be given on the fruit surface in places not covered by previous cuts. The latex collected from all the trees in a day should be pooled, shade dried in an aluminium pan or tray and passed through a 50 mesh sieve to remove all foreign matter. In large plantations, vacuum driers can be adopted with advantage.
Papain produced by artificial heating will have better colour and high quality. Add potassium Meta-bi-sulphite (KMS) at 0.5 % for better colour and keeping quality. The latex should be dried very rapidly at temperatures of 50° to 55° C.
Stop drying when the dried product comes off as flakes having a porous texture. Powder the dried papain by means of wooden mallets or in electrically operated granulators and sieves the powder through 10 mesh sieve.
Pack the powder in polythene bags in convenient quantities and seal them. Put the sealed bags in a tin container and seal it after evacuating air. Exposure to air deteriorates the quality of papain and vacuum sealing is therefore necessary.
For large scale manufacture of papain, vacuum sealing machine and a granulator will be useful. The green papaya fruits after extraction of papain can be used for pectin manufacture and “tutty – fruity” or they can be allowed to ripen and made into other products.
Enzyme present in dried latex of papaya (papin) – Pepsin Papain Yield: 600-800 Kg/ha (crude papain).
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 4. Pomegranate:
a. Botanical name: PunicflgranfltumL. Family: Punicaceae
b. Origin: Iran
c. Soil: Medium loam soil
d. Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of 60 cm x 60 cm x 60 cm size.
e. Planting Space: 6m X 6m
f. Commercial Propagation method: Air layering and Cutting. ik Irrigation: Irrigation is done at 4 days interval.
g. Varieties: Ganesh, Dholka, Jyothi, P-23,26, Muskati red, Alandi, Paper shell, Co 1, Araktha, Spanish, Ruby and Mridhula etc.
(i) Hybrid: 1. Amlidana: Ganesh x Nanha
2. Ruba: Ganesh x Kabul
(ii) Soft-seeded var: Jyothi, Ganesh, Paper shell
(iii) Hard-seeded van Alandi.
Juice of pomegranate is useful for patient suffering from leprosy.
Requirement of Major Nutrients in Different Ages:
1. Flowering time: Ambe bahar – June to Feb.
2. Mrig bahar – June to July.
3. Fruiting time: Feb-June.
4. Major pest: Fruit borer, Aphids and Mites.
5. Major diseases: Fruit rot
6. More incidence of fruit cracking takes place in Mrig bahar season.
7. Yield: 60-75 fruits/tree or 20-25 t/ha/year.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 5. Citrus:
Botanical name: Citrus spp., Family: Rutaceae
Citrus Species:
1. Origin: China, Malaya, India
2. Soil: Loam soil is preferred by citrus species.
3. Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of 75 cm x 75 cm x 75 cm size.
4. Planting Space: 5-6m x 5-6m
5. Planting time:
(a) Acid lime: Dec to Feb and June to Sept.
(b) Sweet orange: July to Sept.
(c) Mandrins: Nov to Dec.
(d) Commercial Propagation Method:
1. Flowering time: Commonly: Feb to March.
Mandrin: Feb. (Amhehahar), June (Mrigbahar) &»Oct. (Haste bahar)
2. Fruiting time: Rainy season.
3. Major pest: Citrus psylla. Fruit sucking moth. Butter fly.
4. Major diseases: Citrus canker. Die back. Citrus gummosis.
5. Yield (average): Lime -150 to 1000 fruits/tree.
Lemon – 300 to 5000 fruits/tree.
Orange and Malta – 5000 fruits/tree.
Mahanibu and Pumelo – 3000 fruits/tree.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 6. Banana:
1. Banana is commonly known as “Adam’s fig, Tree of wisdom, Tree of paradise, Kalpataru (a tree of virtues), Apple of paradise”.
2. Banana is calcifuge and calorific crop (67-130/100gm), moisture loving plant, herbaceous, monocotyledons and monocarpic and triploid fruit crop.
3. Botanical name: Musa paradisiaca and M. sepiantum L., Family: Musaceae
4. Origin: India and China
5. Climate: Tropical & Sub-tropical climate.
6. Soil: Well drained loamy soils are suitable for banana cultivation. Alkaline and saline soils should be avoided.
7. Planting:
(a) Suckers are planted by use of trench method in Tamil Nadu and Furrow method in Gujarat and Maharashtra.
(b) Plant the seedlings in pits of 60 cm x 60 cm x 60 cm size.
8. Planting Space: 1.8m x 1.8m (Basari, Kuhan, jawari)
2.1m X 2.1m (Proven, Rashly, Narendran and Robusta)
9. Commercial Propagation method:
Suckers (Sword Suckers) and Rhizomes.
The selected suckers should be:
(a) Select sword suckers of 500-750gm weight.
(b) Free from diseases and nematodes.
10. Apart from sward suckers, cut rhizomes called ‘Bits’ and ‘peepers’ are also used for propagation.
11. Planting time:
a. Proven, Rashly, Month an, Karpooravalli and Neypoovan – Feb to April.
b. Nendran and Robusta – April to May.
c. Hill Banana – April to May.
12. Irrigation:
Irrigate immediately after planting. Give life saving irrigation after 4 days; subsequent irrigations are to be given once in a week for garden land bananas and once in 10 to 15 days for wetlands. Irrigate the fields copiously after every manure application.
Use drip irrigation @ 5-10 liters/ plant/day from planting to 4th month, 10-15 liters/plant/day from 5th to shooting and 15 liters /plant/day from shooting to till 15 days prior to harvest.
13. Varieties:
Robusta, Lection, Puvan, Hari chhal, Chini champa, Rustavi, Lai keli, H-1, H-2, CO-1, Manthan, Battisa etc.
a. Dessert:
Robusta, Dwarf Cavendish, Grand Nadine, Rashly, Vayal vazhai, Proven, Nendran, Red Banana, Karpooravalli, Col, Matt, Sannachenkadalt, Dayan and Neypoovan are popular varieties in banana. Cavendish groups are generally preferred in export market.
b. Culinary: Month an, Vayal vazhai. Ash Monthand Cahokia.
c. Both Dessert & Culinary purpose: Nendran.
d. Hill areas: Virupakshi, Sirumalai and Namarai, Red Banana.
e. Hybrid: FHIA-1 (Gold finger), CO-1, Proven.
14. Spray micronutrients viz., ZnSO4 (0.5%), FeSO4, (0.2%), CuSO4, (0.2%) and H3BO3 (0.1%) at 3, 5 and 7 month after planting to increase yield and quality of banana. i2r Flowering time: June to July.
15. Fruiting time: Nov-Dec.
16. Intercropping: Leguminous vegetables, beetroot, elephant foot yam and sunhemp can be grown as intercrops. Avoid growing of cucurbitaceous vegetables.
17. Denavelling – Removal of male bud after completion of female phase. De-suckering – Removal of undesired suckers, done once in 45 days of planting.
18.For getting maximum yield, a minimum of 10-12 leaves are required to be retained on the mother plant.
19. Seediness of banana is controlled by spray of 2,4-D @ 25 ppm.
20. Banana cultivars are screened for virus by ELIS A test.
21. Major pest: Weevil and Aphid.
22. Major diseases: Bunchy top, Sigatoka leaf disease and Panama wilt.
23. Finger tip disease is serious in HDP.
24. Tetrazoliurn test for Bunchy top virus detection.
25. Crop duration:
The bunches will be ready for harvest after 12 to 15 months of planting.
26. Harvest:
Bunches attain maturity from 100 to 150 days after flowering depending on variety, soil, weather condition and elevation.
27. Yield (t/ha/year):
a. Poovan: 40-50
b. Month an: 30 – 40
c. Rashly: 40 – 50
d. Robusta: 50 – 60
e. Dwarf Cavendish: 50-60 7)
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 7. Litchi:
1. Litchi is commonly known as “Single seeded nut”.
2. Botanical name: Litchi chine sis L., Family: Sapindaceae
3. Origin: China
4. Climate and Soil: Sub-tropical climate. Prefer sandy loam soil.
5. Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of Im x Im x Im size.
6. Planting Space: 8m X 8m
7. Commercial Propagation method: Air layering and Seed.
8. Rootstock used: Litchi philippinensis
9. Irrigation: Irrigations is applied at 8-10 days interval in winter and 4-5 days interval in summer season.
10. Varieties: Dehradun, Early large red, Late large red, Early seedless, Late seedless. Rose- scented, Bambai, Sahi (suitable for canning), Saharanpur, Calcutta, Gulabi etc.
11. Red pigment – Anthocynin.
a. Flowering time: Oct. to Nov.
b. Flowers are petal less.
c. Fruiting time: March to May.
d. Pulp is the outgrowth of seed in litchi.
e. Major pest: Mites, Mealy bug.
f. Yield: 80-100 kg/tree.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 8. Sapota:
a. Botanical name: Accrues sapota L., Family: Sapindaceae
b. Origin: Mexico
c. Climate and Soil:
Tropical climate and can be grown up to an altitude of 1000 metres. It prefers sandy loam soil.
d. Planting:
Plant the seedlings in pits of 1m x 1m x 1m size.
e. Season of planting: June to December
f. Planting Space: 8m X 8m
g. Commercial Propagation method: Air layering and Inarching.
h. Rootstock used: Rayan, Khirni, Adam’s Apple, Mahua.
i. Irrigation: Irrigation is applied at 8-10 days interval in winter and 4-5 days interval in summer season.
j. Varieties: Kali Patti, Burin Patti, Pile Patti, Oval, Cricket hall, Chari, Abrahams, CO-1,2&3, PKM -1,2,3&4, Guthi, Murrabba etc.
k. Hybrids: CO-1; Cricket ball x oval
PKM-2: Guthi x Kirtibharti
PKM-3: Kalipatti x Cricket ball
DSH-1 & 2: Kalipatti x Cricket ball
Requirement of Major Nutrients in Different Ages _________
Manures and fertilizers maybe applied in September-October at45cmaway from the trunk up to the leaf drip and incorporated.
a. Flowering time: Oct. to Nov.
b. Fruiting time: March to May.
c. Major pest: Mites, Mealy bug.
d. Major diseases: Sooty mould
e. Harvest:
A mature fruit is dull brown in colour and the colour immediately below the skin when scratched is of lighter shade, while in the immature fruits it is green. The mature fruits are harvested by hand picking.
f. Ripening: Ripen the fruits by keeping a beaker containing 5000 ppm Ethrel +10 g NaOH pellets in an air tight chamber. (5 ml Ethrel in one lit of water is 5000 ppm).
g. Yield: 20 – 25 t/ha/year.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 9. Jackfruit:
a. Jackfruit is commonly known as “Monkey jack”.
b. Botanical name: Auto carpus heterophylus L., Family: Moraceae
c. Origin: India
d. Climate and Soil: Tropical climate, prefer sandy loam soil.
e. Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of 1m x 1m x 1m size.
f. Planting Space: 10m x 10m
g. Commercial Propagation method: Seed and Air layering. Seeds are sown immediately after extraction.
h. Irrigation: Once in a week till the plant gets established. Irrigation is applied at 8-10 days interval in winter and 4-5 days interval in summer season.
i. Varieties: Champa, Rudrakshi, Singapore or Ceylon jack, Gulabi, Firm fleshed, Hazari, Soft, Hybrid jack, Panruti selection, Thanjavur jack, Monkey jack are the popular varieties in jack.
Requirement of Major Nutrients in Different Ages:
j. Flowering time: January to Feb.
k. Fruiting time: April to July.
l. Major pest: Shoot borer. Mealy bug.
m. Major diseases: Fruit rot. Leaf spot. Stem rot.
n. Harvest: The yield commences from 5th year in grafts and 8th year in seedling trees. Harvest is done during March-July.
o. Yield: The crop yields about 30-40 t/ha. 10)
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 10. Aonla:
a. Aonla is commonly known as “Malacca tree, Indian Gooseberry”.
b. Botanical name: Phylanthum emblica, Family: Euphorbiaceae
c. Origin: Tropical Asia
d. Climate and Soil: Tropical climate. Prefer light loam soil.
e. Planting: Planting is done in July to August in the pits of 1mx1mx1m size.
Planting Space: 8m X 8m
f. Commercial Propagation method: Inarching and Seed.
g. Irrigation: Irrigation is applied at 4-5 days interval in Irrigation should be avoided during flowering (mid March-mid April).
h. Varieties: Banarasi, Krishna, Chakaiya, Hathijhul, Kanchan, NA-7, 9, 12, BSR- 1etc.
i. Flowering time: Feb to April
j. Fruiting time: July to September.
k. Training and pruning:
Modified central leader system is used for training of aonla. The main branches should be allowed to appear at a height of 0.75-1 m. Above The ground level.Plants should be trained to modified central leader system.Two to four branches with wide crotch angle, appearing in the opposite directions should be encouraged in early years.
During March-April, Prune and thin the crowded branches to provide maximum fruit bearing area in the tree.
l. Yield: 100 qt./tree annually.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 11. Ber:
a. Ber is commonly known as “Poor man’s fruit, king of arid fruits, Chinese fig”.
b. Botanicalname: Zizyphus jujaba, Family: zamnflcefle
c. Origin: India/China
d. Climate: Tropical-Sub tropical climate.
e. Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of 50cm x 50cm x 50cm size.
f. Planting Space: 6m X 6m.
g. Commercial Propagation method: Ring & ‘T’ budding.
h. ‘T’ budding should be done in April to June.
i. Irrigation: Irrigation is applied by basin system of about 4-6 days intervals Irrigation during October causes flowers shedding and that during March. April causes fruit spoilage and delays ripening.
j. Varieties: Banarasi, Kadka banarasi, luaichi, Narma banarasi, Gola Aliguni Paibandi, Umran, Badsah, Ketki, Seb etc.
k. Flowering time: Nov – Dec
l. Fruiting time: Feb – April
m. Training and pruning:
Remove the root stock sprouts and have a straight stem up to 75 cm from the ground level. It is very important in the early years to build up a strong framework and in later years to maintain vigour to improve fruit size and quality. During February – March, prune the trees and thin the crowded branches to provide maximum fruit bearing area in the tree.
n. Best time for pruning – End of May to Mid June.
o. Major pest: Fruit fly. Bark eating caterpillar
p. Major diseases: Powdery mildew. Black tip.
q. Maturity: 5-6 months after flowering.
18. Yield: About 70-80 Kg of fruits/tree/year.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 12. Bael:
a. Botanical name: Aegle marmelos, Family: Rutaceae
b. Richest source of Vit-B2 (Riboflavin).
c. Marmelosin – Active ingredient present in Bael, extracted from bark.
d. Varieties: Kagzi Gonda, Kagzi Etawah, Kagzi Banarasi etc.
e. Harvesting: Matiire green fruits are ideal for harvest.
f. Yield: 18 qt. of good nuts/ha.
g. Ripe fruits are used for beverage making; hence they should be harvested at ripe stage.
h. Mature green fruits are most suitable for making preserve.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 13. Pineapple:
a. Pineapple is a CAM, monocarpic and herbaceous plant.
b. Botanical name: Ananas comosus L., Family: Bromeliaceae ik Origin: Brazil
c. Climate and Soil: Tropical climate. Prefer light soil. ^ Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of 10cm x 10cm x 10cm size. The ideal season for planting is July – September.
d. Planting Space: 60cm x 60cm
e. Commercial Propagation method: Use suckers and slips for planting.
1. Slips-wt.300-400gm
2. Suckers wt.500-700gm.
f. Irrigation: Irrigation is applied at 10-12 days interval in winter and 5-6 days interval in summer season.
g. Varieties: Singapore, Karela, Mauritious, Queen, Lakhat, Morisus, Kexv, Giant Kew, Sugar leaf, Lakhat, Jaldhup etc.
h. Pineapple fruits contain – Bromelin enzyme
i. Aluminium sulphate – best N2 fertilizer for pineapple.
j. Flowering time: Feb to April.
k. Fruiting time: July to September.
l. Ethrel is used for inducing flowering in pineapple.
m. Major pest: Mealy bug.
n. Major diseases: Root rot.
o. Harvest: Fruits can be harvested from 18 to 24 months after planting. Slight colour change at the base of the fruit indicates maturity.
p. Yield: 25-50 tons/ha. One plant crop and two ratoon crops are normally practiced in most of varieties and in Mauritius Varity up to five crops can be taken.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 15. Apple:
a. Apple is commonly known as “Queen of temperate fruit”.
b. Botanical name: Malus pumila L., Family: Rosaceae
c. Origin: Europe, S.E. Asia
d. Himachal Pradesh (HP) is known as “Apple bowl of India”.
e.Climate: Prefer temperate climate.
f. Apple is most widely grown temperate fruit in the world.
g. Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of 1m x 1m x 1m size.
h. Planting Space: 10m x 10m
i. Commercial Propagation method: Tongue grafting and Whip budding.
j. Most critical period for water requirement: April-August
k. Varieties:
i. Early – Summer gold, Early Sunhury, Irish Peach, Pippin (Varieties yields during April – May)
ii. Medium – Orange pippin. King of pippin, Jonethan. (Varieties yields during
iii. Late – Delicious, Rome beauty. Purlin’s Beauty (Varieties yields during August-Sept.) ^
iv. Hybrid – Red gold, Kortled, Spartan.
a. Flower colour: White to Pink.
b. Major pest: Root and stem borer. Leaf eating caterpillar.
c. Major diseases: Brown rot. Powdery mildew.
l. Fruit drop:
i. Early fruit drop: due to lack of pollination.
ii. June drop: due to moisture stress.
iii. Pre-harvest drop: due to development of Abscisic layer, formation of ethylene.
m. Yield:
The yield ranges between 10 – 20 kg / tree / year. The tree starts bearing from 4th year of planting.
n. There are usually 6 size grades of apple.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 16. Peach:
a. Botanical name: Prunus persica. Family: Rosaceae
b. Planting material: One year old budded plants are used as planting material.
c. Planting season: The ideal planting season is June-December.
d. Spacing: For commercial cultivation, the spacing adopted is 4x4m.Planting is done in pits of 60 cm x 60 cm x 60 cm.
e. Varieties: Killikrankie, Floridasun, Shaw Pasand, Red Shanghai.
f. Yield: 10-15 kg of fruits/year.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 17. Pear:
a. Botanical name: Pyrus communis, Family: Rosaceae
b. Planting material: Plant one year old grafts/rooted cuttings.
c. Planting season: The ideal planting season is June to December.
d. Spacing: 5m X 5m or 6m X 6m.
e. Pit size: 60 cm x 60 cm x 60 cm size are taken and the grafts are planted at, the centre of pits.
f. Varieties: Common pear, Kieffer, New Pear, William and Jargonelle are the commonly cultivated Pear varieties.
g. Harvest: Early varieties will come to harvest in May-Juneandlatevarieties in July-October.
h. Yield: 100 to 120 kg/tree/year.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 18 Plum:
a. Botanical name: Prunus selicina. Family: Rosaceae
b. Planting material: One year old budded plants may be planted during June – July or October – December with a spacing of 4 x 4 m m pits of 60 cm X 60 cm X 60 cm size.
c. Planting season: June to November.
d. Varieties: Rubio, Hale, Gaviota, Abundance, Shiro, Kelsey and Satsuma.
e. Yield: 25-30kg/tree/year.
Grape:
a. Botanical name: Vitis vinifera U Family: Vitaceae
b. Origin: Asia/America
c. Climate and Soil: Tropical climate. The crop performs best Rich loamy soil with a pH of 6.5-7.0 with low water table with ECless than 1.0. Soil depth should be at least 1 m.
d. Planting: Planting in pits of 45cm x 45cm x 45cm size in the month of October (ideal time).
e. Planting Space: 2-3m x 2-3m.
For Thompson seedless – (a) spacing of 1.8m x 2.5m is ideal for bower system, (b) spacing of 1.8m x 3.0m is ideal for ‘y’ trelhs system.
f. Commercial Propagation method: Hard wood cutting (Cutting made out from healthy vines in October, Vines should having 5-6 buds).
g. Rootstocks used: Dog ridge, 1613, Slat creek. Temple.
h. Irrigation:
Irrigate immediately after planting and on the 3rd day and then once in a week. Withhold irrigation 15 days before pruning and also 15 days before harvest. Generally, irrigation is applied at 12 days intervals from Nov to January and at 10 days intervals from Feb to March.
i. Varieties:
Black champa (BC), Delight, Bhimasahbi, Bangalore blue, Arka Kanchan, Beauti bedana, Pusa seedless, Anab-e-shahi (AS), Muscat (Panneer), Pachadraksha, Thompson Seedless (TS), Arka Shyam, Arka Hans, Manik Chaman, Sonaka, Sharadh Seedless and Flame Seedless etc.
j. Hybrids: Arkavati; BC x TS
I. Arka Neelmani; BC x TS
II. Arka Hans: Banglore Blue (BE) x Anab-e-shahi
III. Arka Shweta: Anab-e-shahi x TS
IV. Arka Majestic: AS x BC
V. Arka Shyam: BB x BC
k. Foliar spray of 0.1% Boric acid + 0.2% ZnSO^ + 1.0% Urea twice before flowering and 10 days after first spray should be done to overcome nutrient deficiency.
l. Growth regulators:
i. CCC: for suppressing vigour of vine & increase fruit -fullness of bud.
ii. GA3, for increasing berry size.
iii. HCN: to hasten bud break at winter pruning.
iv. NAA (SOppnt): to reduce post harvest fruit drop.
v. MH: for induction of male sterility.
m. Training: Bower system of haining is mostly adopted in India.
The vines are trained with single stem up to pandal with a stalk on tipping at 2 m height. The main arms are developed and trained on opposite directions. On further tipping, secondary and tertiary arms are developed for spreading all over pandal.
n. Pruning:
Weak and immature canes should be pruned to one or two buds to induce vegetative growth.
o. Pruning Season:
1. North India (summer crop): Pruning is done in December – January.
2. South India (Monsoon crop): 2 Pruning is done. 1st in April – May (back or foundation pruning) and 2nd in October.
p. Major pest: Grape vine beetle. Leaf roller, Thrips.
q. Major diseases: Powdery mildew. Downy mildew.
r. Average Yield:
i. Seedless: 15 t/ ha/ year
ii. Muscat: 30 t/ ha/ year
iii. Pachadraksha: 40 t /ha/year
iv. Anab-e-Shahi and Arka hybrids: 20 t/ ha/year
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 20. Coconut:
a. Coconut is commonly known as “Kalpavriksha”.
b. Botanical name: Cocus nucifera L., Family: Cocoidae
c. Origin: South East Asia
d. Climate and Soil: Tropical climate. Prefer sandy to heavy clay or alluvial soil.
e. Sowing:
f. Nursery:
g. Planting: Plant the seedlings in pits of Im x Im x Im size.
h. Planting Space: Nut to nut spacing is 30 cm and row to row spacing is 50cm.
i. Commercial Propagation method: Nuts.
j. Irrigation: Irrigation is applied by basin system of about 60 litre/week.
k. Varieties: East coastal tall. West coastal tall, Malayan dwarf, Banawali, Fizi, Pratap etc.
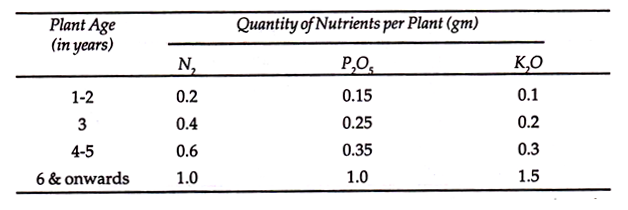
Requirement of Major Nutrients in Different Ages:
Plant Age (in years)Quantity of Nutrients per Plant (gm)
l. Yield: 40-200 nuts/ha.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 21. Arecanut:
a. Botanical name: Areca catechu, Family: Arecaceae
b. Origin: Indian Ocean
c. Climate and Soil: Humid climate with favouring shaded condition, Prefer alluvial laon soil
d. Planting Space: 10m x 10m
e. Commercial Propagation Method: Seeds
f. Varieties: South Kanara, Srivardhan, Mangala. VTL-3, 11, 17 etc.
Fruit Crop: Cultivation # 22. Karonda:
a. Botanical name: Carissa caranda
b. Richest source of Iron and behave as Xerophytic Plant.
c. Spacing: 2m x 2m
d. Varieties: Maroon etc.
e. Yield: 2-4 kg/tree